David Iben put it well when he said, 'Volatility is not a risk we care about. What we care about is avoiding the permanent loss of capital.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. We can see that Shenzhen Expressway Corporation Limited (HKG:548) does use debt in its business. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, debt can be an important tool in businesses, particularly capital heavy businesses. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
See our latest analysis for Shenzhen Expressway
What Is Shenzhen Expressway's Net Debt?
As you can see below, at the end of March 2022, Shenzhen Expressway had CN¥34.4b of debt, up from CN¥23.2b a year ago. Click the image for more detail. On the flip side, it has CN¥6.21b in cash leading to net debt of about CN¥28.2b.
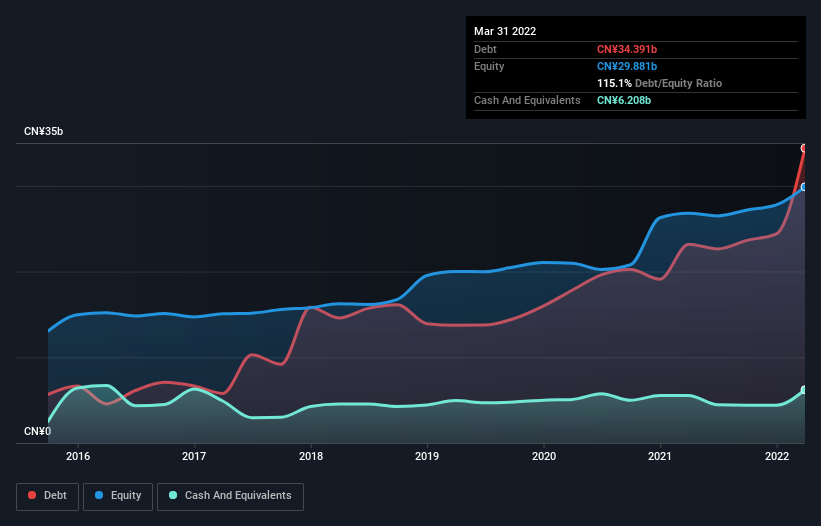
How Healthy Is Shenzhen Expressway's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Shenzhen Expressway had liabilities of CN¥17.0b due within 12 months, and liabilities of CN¥24.7b due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of CN¥6.21b as well as receivables valued at CN¥1.97b due within 12 months. So its liabilities total CN¥33.6b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
This deficit casts a shadow over the CN¥18.9b company, like a colossus towering over mere mortals. So we definitely think shareholders need to watch this one closely. After all, Shenzhen Expressway would likely require a major re-capitalisation if it had to pay its creditors today.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Strangely Shenzhen Expressway has a sky high EBITDA ratio of 5.5, implying high debt, but a strong interest coverage of 10.0. So either it has access to very cheap long term debt or that interest expense is going to grow! Unfortunately, Shenzhen Expressway's EBIT flopped 10% over the last four quarters. If that sort of decline is not arrested, then the managing its debt will be harder than selling broccoli flavoured ice-cream for a premium. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Shenzhen Expressway can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. Considering the last three years, Shenzhen Expressway actually recorded a cash outflow, overall. Debt is usually more expensive, and almost always more risky in the hands of a company with negative free cash flow. Shareholders ought to hope for an improvement.
Our View
To be frank both Shenzhen Expressway's conversion of EBIT to free cash flow and its track record of staying on top of its total liabilities make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. But at least it's pretty decent at covering its interest expense with its EBIT; that's encouraging. We should also note that Infrastructure industry companies like Shenzhen Expressway commonly do use debt without problems. Taking into account all the aforementioned factors, it looks like Shenzhen Expressway has too much debt. That sort of riskiness is ok for some, but it certainly doesn't float our boat. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. For instance, we've identified 2 warning signs for Shenzhen Expressway (1 is concerning) you should be aware of.
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About SEHK:548
Shenzhen Expressway
Primarily invests in, constructs, operates, and manages toll highways and roads, as well as other urban and transportation infrastructure in the People’s Republic of China.
Slight second-rate dividend payer.
Market Insights
Community Narratives





