
The external fund manager backed by Berkshire Hathaway's Charlie Munger, Li Lu, makes no bones about it when he says 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. We note that H+H International A/S (CPH:HH) does have debt on its balance sheet. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. Part and parcel of capitalism is the process of 'creative destruction' where failed businesses are mercilessly liquidated by their bankers. While that is not too common, we often do see indebted companies permanently diluting shareholders because lenders force them to raise capital at a distressed price. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for H+H International
What Is H+H International's Net Debt?
As you can see below, at the end of December 2020, H+H International had kr.609.0m of debt, up from kr.558.0m a year ago. Click the image for more detail. However, it does have kr.481.0m in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about kr.128.0m.
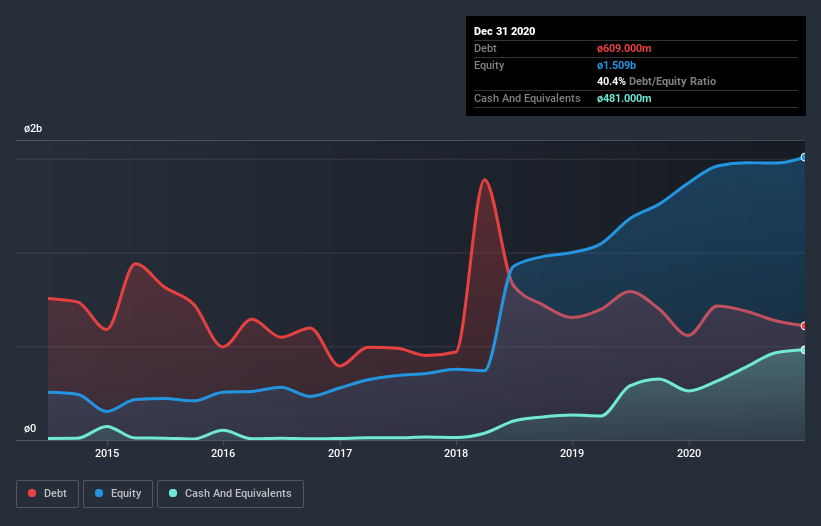
How Healthy Is H+H International's Balance Sheet?
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that H+H International had liabilities of kr.396.0m due within 12 months and liabilities of kr.1.00b due beyond that. Offsetting this, it had kr.481.0m in cash and kr.109.0m in receivables that were due within 12 months. So its liabilities total kr.810.0m more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
H+H International has a market capitalization of kr.2.97b, so it could very likely raise cash to ameliorate its balance sheet, if the need arose. But we definitely want to keep our eyes open to indications that its debt is bringing too much risk.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
H+H International's net debt is only 0.25 times its EBITDA. And its EBIT covers its interest expense a whopping 23.8 times over. So you could argue it is no more threatened by its debt than an elephant is by a mouse. On the other hand, H+H International saw its EBIT drop by 8.3% in the last twelve months. If earnings continue to decline at that rate the company may have increasing difficulty managing its debt load. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine H+H International's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. Over the last three years, H+H International recorded free cash flow worth a fulsome 82% of its EBIT, which is stronger than we'd usually expect. That puts it in a very strong position to pay down debt.
Our View
H+H International's interest cover suggests it can handle its debt as easily as Cristiano Ronaldo could score a goal against an under 14's goalkeeper. But truth be told we feel its EBIT growth rate does undermine this impression a bit. Taking all this data into account, it seems to us that H+H International takes a pretty sensible approach to debt. That means they are taking on a bit more risk, in the hope of boosting shareholder returns. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. To that end, you should be aware of the 1 warning sign we've spotted with H+H International .
When all is said and done, sometimes its easier to focus on companies that don't even need debt. Readers can access a list of growth stocks with zero net debt 100% free, right now.
If you’re looking to trade H+H International, open an account with the lowest-cost* platform trusted by professionals, Interactive Brokers. Their clients from over 200 countries and territories trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account. Promoted
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if H+H International might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisThis article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About CPSE:HH
H+H International
Provides wall building materials and solutions in the United Kingdom, Central Western Europe, and Poland.
Undervalued with moderate growth potential.
Market Insights
Community Narratives




