The external fund manager backed by Berkshire Hathaway's Charlie Munger, Li Lu, makes no bones about it when he says 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We can see that Trina Solar Co., Ltd. (SHSE:688599) does use debt in its business. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for Trina Solar
What Is Trina Solar's Debt?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that as of September 2024 Trina Solar had CN¥50.5b of debt, an increase on CN¥34.4b, over one year. On the flip side, it has CN¥26.3b in cash leading to net debt of about CN¥24.2b.
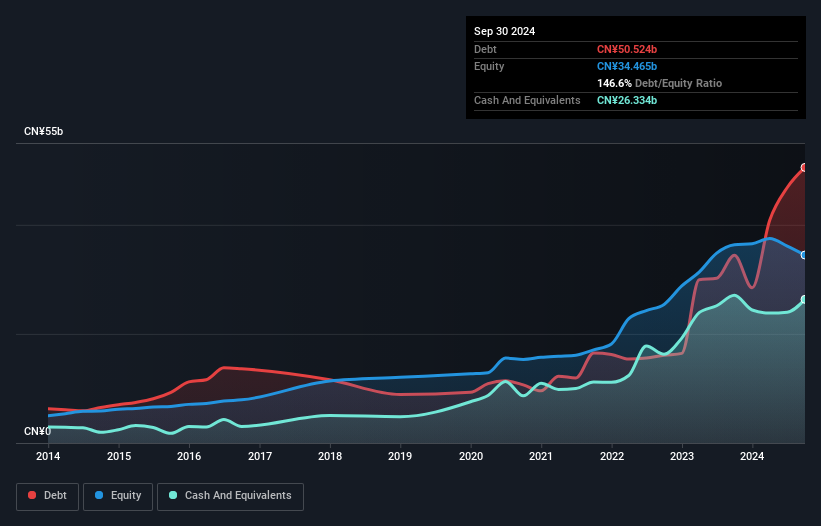
How Healthy Is Trina Solar's Balance Sheet?
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that Trina Solar had liabilities of CN¥62.1b due within 12 months and liabilities of CN¥39.0b due beyond that. On the other hand, it had cash of CN¥26.3b and CN¥22.3b worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities total CN¥52.5b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
When you consider that this deficiency exceeds the company's CN¥49.7b market capitalization, you might well be inclined to review the balance sheet intently. Hypothetically, extremely heavy dilution would be required if the company were forced to pay down its liabilities by raising capital at the current share price.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
While we wouldn't worry about Trina Solar's net debt to EBITDA ratio of 4.2, we think its super-low interest cover of 1.4 times is a sign of high leverage. It seems that the business incurs large depreciation and amortisation charges, so maybe its debt load is heavier than it would first appear, since EBITDA is arguably a generous measure of earnings. So shareholders should probably be aware that interest expenses appear to have really impacted the business lately. Even worse, Trina Solar saw its EBIT tank 78% over the last 12 months. If earnings continue to follow that trajectory, paying off that debt load will be harder than convincing us to run a marathon in the rain. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Trina Solar's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Over the last three years, Trina Solar reported free cash flow worth 5.4% of its EBIT, which is really quite low. For us, cash conversion that low sparks a little paranoia about is ability to extinguish debt.
Our View
On the face of it, Trina Solar's interest cover left us tentative about the stock, and its EBIT growth rate was no more enticing than the one empty restaurant on the busiest night of the year. And furthermore, its level of total liabilities also fails to instill confidence. Taking into account all the aforementioned factors, it looks like Trina Solar has too much debt. While some investors love that sort of risky play, it's certainly not our cup of tea. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. For example, we've discovered 3 warning signs for Trina Solar (2 are a bit unpleasant!) that you should be aware of before investing here.
If you're interested in investing in businesses that can grow profits without the burden of debt, then check out this free list of growing businesses that have net cash on the balance sheet.
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Trina Solar might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About SHSE:688599
Trina Solar
Engages in the research and development, production, and sales of photovoltaic (PV) modules in China, Europe, North America, South America, Japan, the Asia Pacific, the Middle East, and North Africa.
Reasonable growth potential and fair value.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



