Here's What You Should Know About Exchange Income Corporation's (TSE:EIF) 5.9% Dividend Yield
Is Exchange Income Corporation (TSE:EIF) a good dividend stock? How can we tell? Dividend paying companies with growing earnings can be highly rewarding in the long term. Yet sometimes, investors buy a popular dividend stock because of its yield, and then lose money if the company's dividend doesn't live up to expectations.
In this case, Exchange Income likely looks attractive to investors, given its 5.9% dividend yield and a payment history of over ten years. It would not be a surprise to discover that many investors buy it for the dividends. When buying stocks for their dividends, you should always run through the checks below, to see if the dividend looks sustainable.
Click the interactive chart for our full dividend analysis
Payout ratios
Companies (usually) pay dividends out of their earnings. If a company is paying more than it earns, the dividend might have to be cut. Comparing dividend payments to a company's net profit after tax is a simple way of reality-checking whether a dividend is sustainable. In the last year, Exchange Income paid out 96% of its profit as dividends. Its payout ratio is quite high, and the dividend is not well covered by earnings. If earnings are growing or the company has a large cash balance, this might be sustainable - still, we think it is a concern.
We also measure dividends paid against a company's levered free cash flow, to see if enough cash was generated to cover the dividend. Unfortunately, while Exchange Income pays a dividend, it also reported negative free cash flow last year. While there may be a good reason for this, it's not ideal from a dividend perspective.
Is Exchange Income's Balance Sheet Risky?
As Exchange Income's dividend was not well covered by earnings, we need to check its balance sheet for signs of financial distress. A quick check of its financial situation can be done with two ratios: net debt divided by EBITDA (earnings before interest, tax, depreciation and amortisation), and net interest cover. Net debt to EBITDA measures total debt load relative to company earnings (lower = less debt), while net interest cover measures the ability to pay interest on the debt (higher = greater ability to pay interest costs). Exchange Income has net debt of 3.50 times its EBITDA, which is getting towards the limit of most investors' comfort zones. Judicious use of debt can enhance shareholder returns, but also adds to the risk if something goes awry.
Net interest cover can be calculated by dividing earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) by the company's net interest expense. Interest cover of 2.62 times its interest expense is starting to become a concern for Exchange Income, and be aware that lenders may place additional restrictions on the company as well.
Dividend Volatility
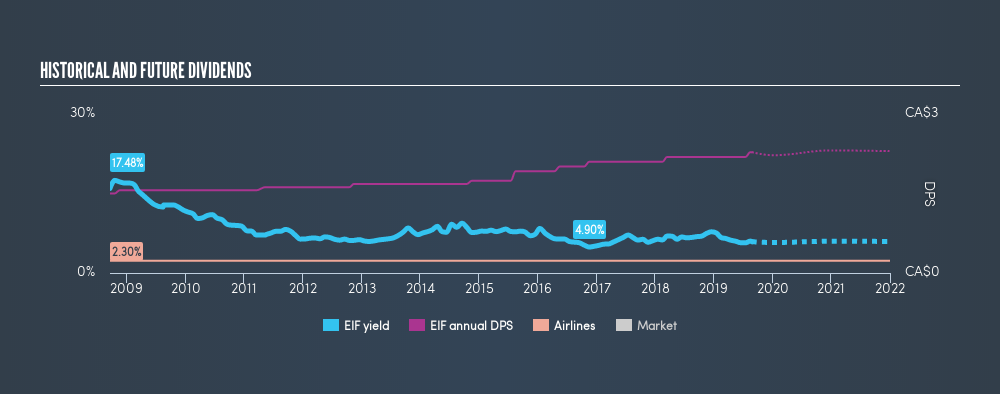
One of the major risks of relying on dividend income, is the potential for a company to struggle financially and cut its dividend. Not only is your income cut, but the value of your investment declines as well - nasty. For the purpose of this article, we only scrutinise the last decade of Exchange Income's dividend payments. During this period the dividend has been stable, which could imply the business could have relatively consistent earnings power. During the past ten-year period, the first annual payment was CA$1.50 in 2009, compared to CA$2.28 last year. Dividends per share have grown at approximately 4.3% per year over this time.
Slow and steady dividend growth might not sound that exciting, but dividends have been stable for ten years, which we think is seriously impressive.
Dividend Growth Potential
Dividend payments have been consistent over the past few years, but we should always check if earnings per share (EPS) are growing, as this will help maintain the purchasing power of the dividend. It's good to see Exchange Income has been growing its earnings per share at 36% a year over the past 5 years. The company has been growing its EPS at a very rapid rate, while paying out virtually all of its income as dividends. Generally, a company that is growing rapidly while paying out a majority of its earnings, is seeing its debt burden increase. We'd be conscious of any extra risk added by this practice.
Conclusion
When we look at a dividend stock, we need to form a judgement on whether the dividend will grow, if the company is able to maintain it in a wide range of economic circumstances, and if the dividend payout is sustainable. We're a bit uncomfortable with Exchange Income paying out a high percentage of both its cashflow and earnings. It hasn't demonstrated a strong ability to grow earnings per share, but we like that the dividend payments have been fairly consistent. Ultimately, Exchange Income comes up short on our dividend analysis. It's not that we think it is a bad company - just that there are likely more appealing dividend prospects out there on this analysis.
Companies that are growing earnings tend to be the best dividend stocks over the long term. See what the 11 analysts we track are forecasting for Exchange Income for free with public analyst estimates for the company.
We have also put together a list of global stocks with a market capitalisation above $1bn and yielding more 3%.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned. Thank you for reading.
About TSX:EIF
Exchange Income
Engages in aerospace and aviation services and equipment, and manufacturing businesses worldwide.
Reasonable growth potential with proven track record.
Market Insights
Community Narratives




