David Iben put it well when he said, 'Volatility is not a risk we care about. What we care about is avoiding the permanent loss of capital.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. Importantly, Trisul S.A. (BVMF:TRIS3) does carry debt. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
Check out the opportunities and risks within the BR Consumer Durables industry.
What Is Trisul's Debt?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at June 2022 Trisul had debt of R$657.0m, up from R$475.0m in one year. However, it does have R$325.5m in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about R$331.5m.
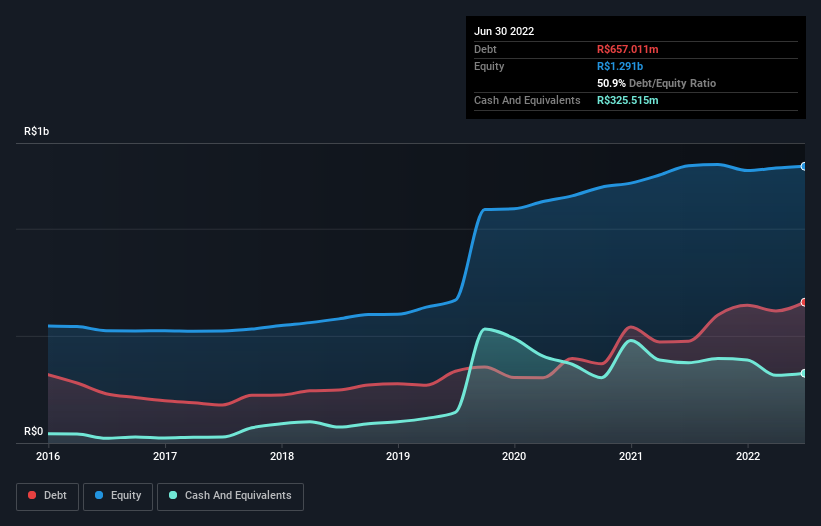
A Look At Trisul's Liabilities
We can see from the most recent balance sheet that Trisul had liabilities of R$447.2m falling due within a year, and liabilities of R$570.5m due beyond that. Offsetting this, it had R$325.5m in cash and R$297.6m in receivables that were due within 12 months. So its liabilities total R$394.6m more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
Trisul has a market capitalization of R$924.5m, so it could very likely raise cash to ameliorate its balance sheet, if the need arose. But it's clear that we should definitely closely examine whether it can manage its debt without dilution.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Trisul's net debt of 2.5 times EBITDA suggests graceful use of debt. And the alluring interest cover (EBIT of 7.3 times interest expense) certainly does not do anything to dispel this impression. Importantly, Trisul's EBIT fell a jaw-dropping 43% in the last twelve months. If that decline continues then paying off debt will be harder than selling foie gras at a vegan convention. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Trisul's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. During the last three years, Trisul burned a lot of cash. While investors are no doubt expecting a reversal of that situation in due course, it clearly does mean its use of debt is more risky.
Our View
To be frank both Trisul's conversion of EBIT to free cash flow and its track record of (not) growing its EBIT make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. But at least it's pretty decent at covering its interest expense with its EBIT; that's encouraging. We're quite clear that we consider Trisul to be really rather risky, as a result of its balance sheet health. So we're almost as wary of this stock as a hungry kitten is about falling into its owner's fish pond: once bitten, twice shy, as they say. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. We've identified 3 warning signs with Trisul , and understanding them should be part of your investment process.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
The New Payments ETF Is Live on NASDAQ:
Money is moving to real-time rails, and a newly listed ETF now gives investors direct exposure. Fast settlement. Institutional custody. Simple access.
Explore how this launch could reshape portfolios
Sponsored ContentValuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Trisul might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About BOVESPA:TRIS3
Trisul
Engages in the construction and development of real estate properties in Brazil.
Proven track record with adequate balance sheet and pays a dividend.
Market Insights
Weekly Picks

Early mover in a fast growing industry. Likely to experience share price volatility as they scale


A case for CA$31.80 (undiluted), aka 8,616% upside from CA$0.37 (an 86 bagger!).


Moderation and Stabilisation: HOLD: Fair Price based on a 4-year Cycle is $12.08
Recently Updated Narratives

Airbnb Stock: Platform Growth in a World of Saturation and Scrutiny

Adobe Stock: AI-Fueled ARR Growth Pushes Guidance Higher, But Cost Pressures Loom

Thomson Reuters Stock: When Legal Intelligence Becomes Mission-Critical Infrastructure
Popular Narratives


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026


The AI Infrastructure Giant Grows Into Its Valuation
Trending Discussion




