Today we are going to look at CSR Limited (ASX:CSR) to see whether it might be an attractive investment prospect. Specifically, we're going to calculate its Return On Capital Employed (ROCE), in the hopes of getting some insight into the business.
First, we'll go over how we calculate ROCE. Next, we'll compare it to others in its industry. Finally, we'll look at how its current liabilities affect its ROCE.
What is Return On Capital Employed (ROCE)?
ROCE measures the 'return' (pre-tax profit) a company generates from capital employed in its business. Generally speaking a higher ROCE is better. Ultimately, it is a useful but imperfect metric. Author Edwin Whiting says to be careful when comparing the ROCE of different businesses, since 'No two businesses are exactly alike.'
So, How Do We Calculate ROCE?
Analysts use this formula to calculate return on capital employed:
Return on Capital Employed = Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) ÷ (Total Assets - Current Liabilities)
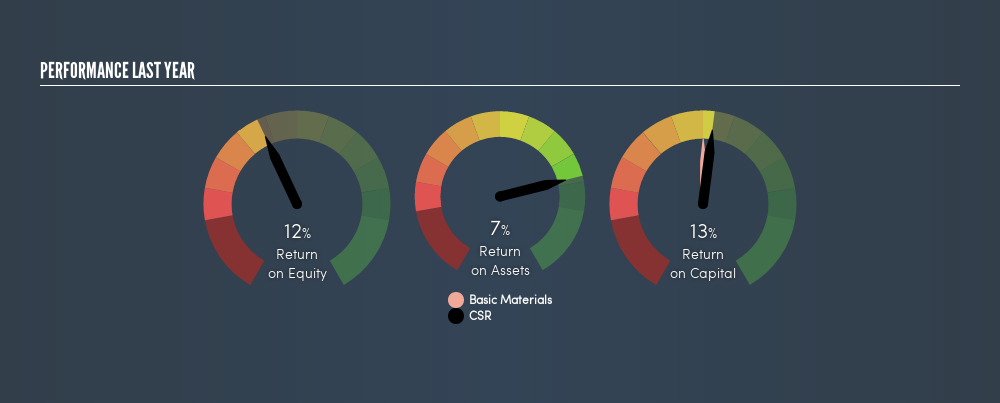
Or for CSR:
0.13 = AU$200m ÷ (AU$2.0b - AU$440m) (Based on the trailing twelve months to March 2019.)
So, CSR has an ROCE of 13%.
Check out our latest analysis for CSR
Is CSR's ROCE Good?
ROCE is commonly used for comparing the performance of similar businesses. Using our data, CSR's ROCE appears to be around the 11% average of the Basic Materials industry. Separate from CSR's performance relative to its industry, its ROCE in absolute terms looks satisfactory, and it may be worth researching in more depth.
When considering ROCE, bear in mind that it reflects the past and does not necessarily predict the future. ROCE can be deceptive for cyclical businesses, as returns can look incredible in boom times, and terribly low in downturns. ROCE is, after all, simply a snap shot of a single year. Future performance is what matters, and you can see analyst predictions in our free report on analyst forecasts for the company.
CSR's Current Liabilities And Their Impact On Its ROCE
Liabilities, such as supplier bills and bank overdrafts, are referred to as current liabilities if they need to be paid within 12 months. Due to the way the ROCE equation works, having large bills due in the near term can make it look as though a company has less capital employed, and thus a higher ROCE than usual. To counteract this, we check if a company has high current liabilities, relative to its total assets.
CSR has total assets of AU$2.0b and current liabilities of AU$440m. As a result, its current liabilities are equal to approximately 22% of its total assets. A fairly low level of current liabilities is not influencing the ROCE too much.
Our Take On CSR's ROCE
This is good to see, and with a sound ROCE, CSR could be worth a closer look. CSR shapes up well under this analysis, but it is far from the only business delivering excellent numbers . You might also want to check this free collection of companies delivering excellent earnings growth.
For those who like to find winning investments this free list of growing companies with recent insider purchasing, could be just the ticket.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned. Thank you for reading.
About ASX:CSR
CSR
Engages in the manufacture and supply of building products for residential and commercial constructions in Australia and New Zealand.
Flawless balance sheet and slightly overvalued.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



