- United States
- /
- Food and Staples Retail
- /
- NYSE:DG
Dollar General (NYSE:DG) Takes On Some Risk With Its Use Of Debt
David Iben put it well when he said, 'Volatility is not a risk we care about. What we care about is avoiding the permanent loss of capital.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. As with many other companies Dollar General Corporation (NYSE:DG) makes use of debt. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, debt can be an important tool in businesses, particularly capital heavy businesses. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
Check out our latest analysis for Dollar General
How Much Debt Does Dollar General Carry?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at November 2023 Dollar General had debt of US$7.19b, up from US$5.99b in one year. However, it also had US$365.4m in cash, and so its net debt is US$6.83b.
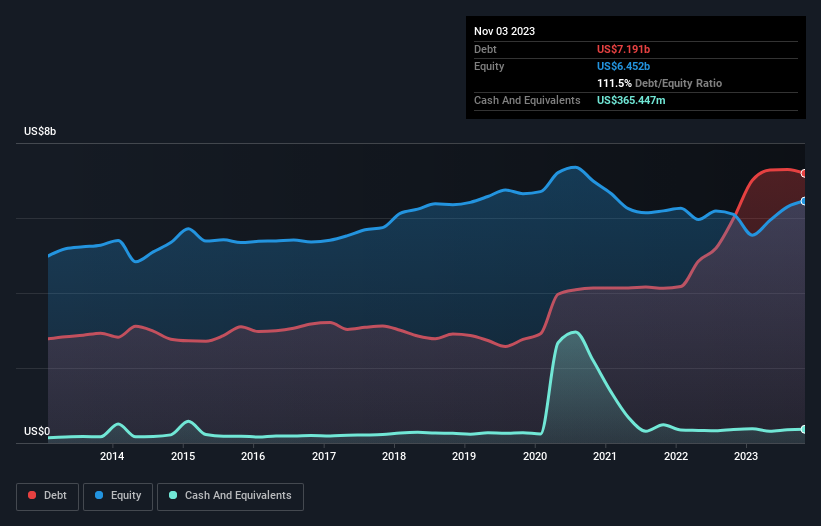
How Strong Is Dollar General's Balance Sheet?
The latest balance sheet data shows that Dollar General had liabilities of US$6.79b due within a year, and liabilities of US$17.4b falling due after that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of US$365.4m as well as receivables valued at US$197.6m due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by US$23.6b.
This deficit is considerable relative to its very significant market capitalization of US$29.6b, so it does suggest shareholders should keep an eye on Dollar General's use of debt. Should its lenders demand that it shore up the balance sheet, shareholders would likely face severe dilution.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
With a debt to EBITDA ratio of 1.9, Dollar General uses debt artfully but responsibly. And the alluring interest cover (EBIT of 8.6 times interest expense) certainly does not do anything to dispel this impression. Unfortunately, Dollar General's EBIT flopped 13% over the last four quarters. If earnings continue to decline at that rate then handling the debt will be more difficult than taking three children under 5 to a fancy pants restaurant. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Dollar General can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, while the tax-man may adore accounting profits, lenders only accept cold hard cash. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. In the last three years, Dollar General's free cash flow amounted to 28% of its EBIT, less than we'd expect. That's not great, when it comes to paying down debt.
Our View
On the face of it, Dollar General's level of total liabilities left us tentative about the stock, and its EBIT growth rate was no more enticing than the one empty restaurant on the busiest night of the year. But on the bright side, its interest cover is a good sign, and makes us more optimistic. Once we consider all the factors above, together, it seems to us that Dollar General's debt is making it a bit risky. That's not necessarily a bad thing, but we'd generally feel more comfortable with less leverage. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. We've identified 2 warning signs with Dollar General , and understanding them should be part of your investment process.
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About NYSE:DG
Dollar General
A discount retailer, provides various merchandise products in the southern, southwestern, midwestern, and eastern United States.
Undervalued established dividend payer.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



