Some say volatility, rather than debt, is the best way to think about risk as an investor, but Warren Buffett famously said that 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. As with many other companies Taiwan Semiconductor Co., Ltd. (GTSM:5425) makes use of debt. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more common (but still painful) scenario is that it has to raise new equity capital at a low price, thus permanently diluting shareholders. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Taiwan Semiconductor
What Is Taiwan Semiconductor's Net Debt?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that Taiwan Semiconductor had NT$3.48b of debt in December 2020, down from NT$3.66b, one year before. On the flip side, it has NT$3.05b in cash leading to net debt of about NT$435.0m.
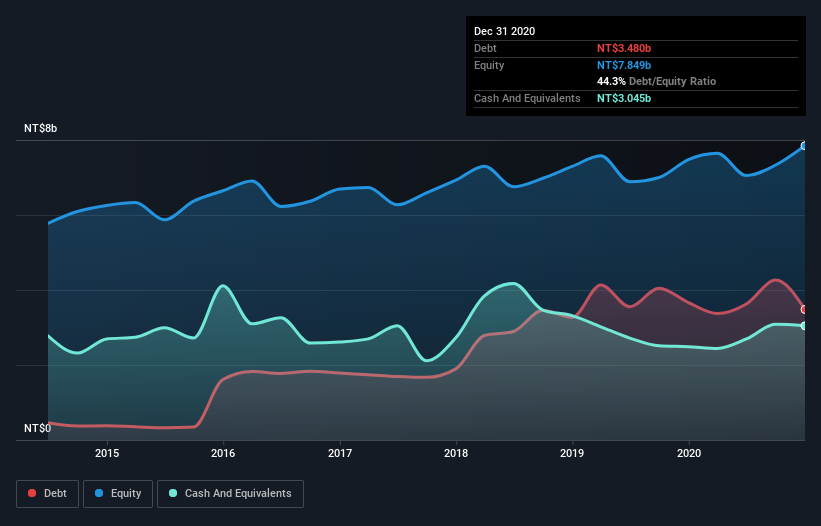
How Strong Is Taiwan Semiconductor's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Taiwan Semiconductor had liabilities of NT$4.54b due within 12 months, and liabilities of NT$2.24b due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of NT$3.05b as well as receivables valued at NT$2.42b due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling NT$1.32b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
Given Taiwan Semiconductor has a market capitalization of NT$14.0b, it's hard to believe these liabilities pose much threat. But there are sufficient liabilities that we would certainly recommend shareholders continue to monitor the balance sheet, going forward.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
Taiwan Semiconductor has a low net debt to EBITDA ratio of only 0.22. And its EBIT covers its interest expense a whopping 58.3 times over. So we're pretty relaxed about its super-conservative use of debt. But the other side of the story is that Taiwan Semiconductor saw its EBIT decline by 2.7% over the last year. If earnings continue to decline at that rate the company may have increasing difficulty managing its debt load. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Taiwan Semiconductor's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Over the most recent three years, Taiwan Semiconductor recorded free cash flow worth 52% of its EBIT, which is around normal, given free cash flow excludes interest and tax. This free cash flow puts the company in a good position to pay down debt, when appropriate.
Our View
Taiwan Semiconductor's interest cover suggests it can handle its debt as easily as Cristiano Ronaldo could score a goal against an under 14's goalkeeper. But, on a more sombre note, we are a little concerned by its EBIT growth rate. All these things considered, it appears that Taiwan Semiconductor can comfortably handle its current debt levels. Of course, while this leverage can enhance returns on equity, it does bring more risk, so it's worth keeping an eye on this one. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. These risks can be hard to spot. Every company has them, and we've spotted 4 warning signs for Taiwan Semiconductor (of which 1 is significant!) you should know about.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
If you’re looking to trade a wide range of investments, open an account with the lowest-cost* platform trusted by professionals, Interactive Brokers. Their clients from over 200 countries and territories trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account. Promoted
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Taiwan Semiconductor might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisThis article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About TPEX:5425
Taiwan Semiconductor
Manufactures and sells rectifiers and bar code printers in Asia, the United States, Europe, and internationally.
Flawless balance sheet with acceptable track record.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Weekly Picks


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)


Fiducian: Compliance Clouds or Value Opportunity?

Willamette Valley Vineyards (WVVI): Not-So-Great Value
Recently Updated Narratives

THE KINGDOM OF BROWN GOODS: WHY MGPI IS BEING CRUSHED BY INVENTORY & PRIMED FOR RESURRECTION


The "Molecular Pencil": Why Beam's Technology is Built to Win


ADNOC Gas future shines with a 21.4% revenue surge
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026





