- Taiwan
- /
- Basic Materials
- /
- TWSE:1102
These 4 Measures Indicate That Asia Cement (TWSE:1102) Is Using Debt Reasonably Well

The external fund manager backed by Berkshire Hathaway's Charlie Munger, Li Lu, makes no bones about it when he says 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We can see that Asia Cement Corporation (TWSE:1102) does use debt in its business. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. While that is not too common, we often do see indebted companies permanently diluting shareholders because lenders force them to raise capital at a distressed price. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Asia Cement
What Is Asia Cement's Debt?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that Asia Cement had NT$101.5b of debt in September 2024, down from NT$117.8b, one year before. On the flip side, it has NT$91.0b in cash leading to net debt of about NT$10.5b.
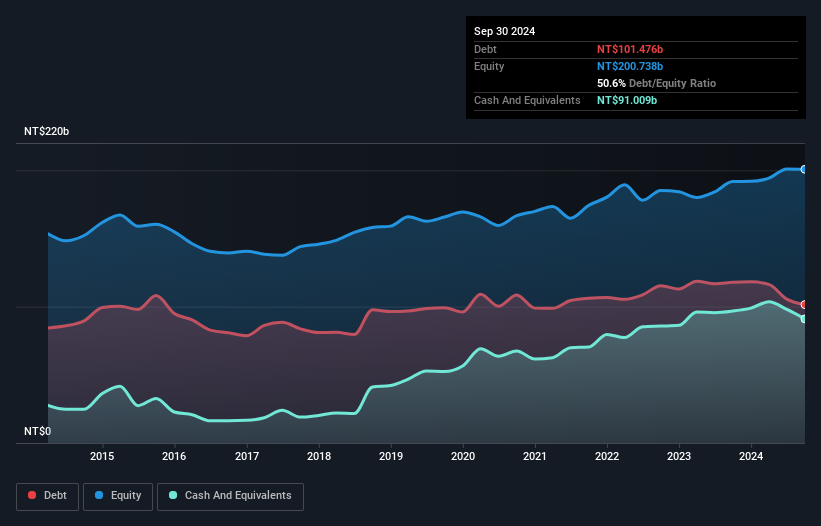
How Healthy Is Asia Cement's Balance Sheet?
The latest balance sheet data shows that Asia Cement had liabilities of NT$77.5b due within a year, and liabilities of NT$50.5b falling due after that. On the other hand, it had cash of NT$91.0b and NT$14.0b worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities total NT$23.0b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
Given Asia Cement has a market capitalization of NT$139.9b, it's hard to believe these liabilities pose much threat. Having said that, it's clear that we should continue to monitor its balance sheet, lest it change for the worse.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Asia Cement has a low debt to EBITDA ratio of only 1.00. But the really cool thing is that it actually managed to receive more interest than it paid, over the last year. So it's fair to say it can handle debt like a hotshot teppanyaki chef handles cooking. But the bad news is that Asia Cement has seen its EBIT plunge 12% in the last twelve months. We think hat kind of performance, if repeated frequently, could well lead to difficulties for the stock. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Asia Cement's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, while the tax-man may adore accounting profits, lenders only accept cold hard cash. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. Over the last three years, Asia Cement actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT. That sort of strong cash conversion gets us as excited as the crowd when the beat drops at a Daft Punk concert.
Our View
The good news is that Asia Cement's demonstrated ability to cover its interest expense with its EBIT delights us like a fluffy puppy does a toddler. But the stark truth is that we are concerned by its EBIT growth rate. All these things considered, it appears that Asia Cement can comfortably handle its current debt levels. Of course, while this leverage can enhance returns on equity, it does bring more risk, so it's worth keeping an eye on this one. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. Case in point: We've spotted 2 warning signs for Asia Cement you should be aware of.
If, after all that, you're more interested in a fast growing company with a rock-solid balance sheet, then check out our list of net cash growth stocks without delay.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About TWSE:1102
Asia Cement
Engages in the manufacturing and selling cement, clinker, ready-mixed concrete, and cement related products in China and Taiwan.
Flawless balance sheet average dividend payer.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives




