- Singapore
- /
- Commercial Services
- /
- SGX:5NV
Chasen Holdings (SGX:5NV) Has A Somewhat Strained Balance Sheet
The external fund manager backed by Berkshire Hathaway's Charlie Munger, Li Lu, makes no bones about it when he says 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We note that Chasen Holdings Limited (SGX:5NV) does have debt on its balance sheet. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Having said that, the most common situation is where a company manages its debt reasonably well - and to its own advantage. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Chasen Holdings
How Much Debt Does Chasen Holdings Carry?
As you can see below, Chasen Holdings had S$64.8m of debt, at September 2023, which is about the same as the year before. You can click the chart for greater detail. On the flip side, it has S$21.1m in cash leading to net debt of about S$43.6m.
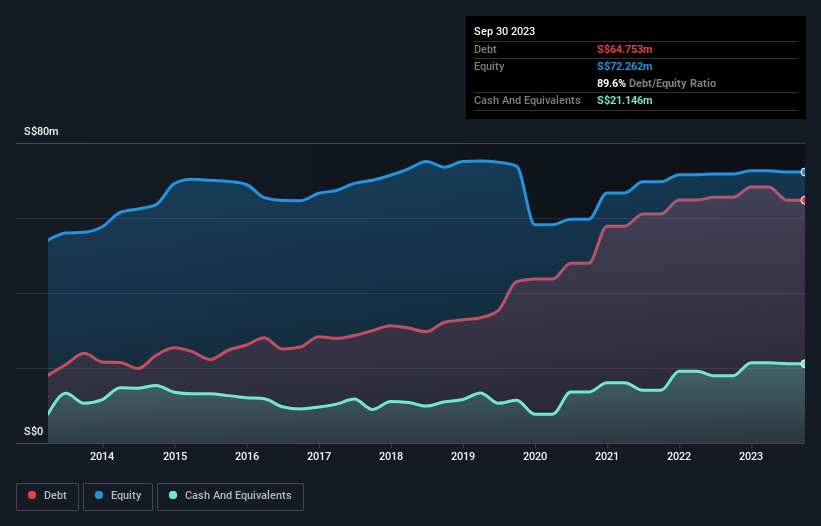
How Strong Is Chasen Holdings' Balance Sheet?
The latest balance sheet data shows that Chasen Holdings had liabilities of S$90.8m due within a year, and liabilities of S$50.0m falling due after that. Offsetting this, it had S$21.1m in cash and S$74.0m in receivables that were due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling S$45.6m more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
The deficiency here weighs heavily on the S$29.8m company itself, as if a child were struggling under the weight of an enormous back-pack full of books, his sports gear, and a trumpet. So we definitely think shareholders need to watch this one closely. After all, Chasen Holdings would likely require a major re-capitalisation if it had to pay its creditors today.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
While Chasen Holdings's debt to EBITDA ratio (2.7) suggests that it uses some debt, its interest cover is very weak, at 1.8, suggesting high leverage. It seems clear that the cost of borrowing money is negatively impacting returns for shareholders, of late. The good news is that Chasen Holdings grew its EBIT a smooth 37% over the last twelve months. Like a mother's loving embrace of a newborn that sort of growth builds resilience, putting the company in a stronger position to manage its debt. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But you can't view debt in total isolation; since Chasen Holdings will need earnings to service that debt. So if you're keen to discover more about its earnings, it might be worth checking out this graph of its long term earnings trend.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. Happily for any shareholders, Chasen Holdings actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT over the last three years. That sort of strong cash generation warms our hearts like a puppy in a bumblebee suit.
Our View
We feel some trepidation about Chasen Holdings's difficulty level of total liabilities, but we've got positives to focus on, too. For example, its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow and EBIT growth rate give us some confidence in its ability to manage its debt. We think that Chasen Holdings's debt does make it a bit risky, after considering the aforementioned data points together. That's not necessarily a bad thing, since leverage can boost returns on equity, but it is something to be aware of. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. We've identified 3 warning signs with Chasen Holdings (at least 2 which don't sit too well with us) , and understanding them should be part of your investment process.
When all is said and done, sometimes its easier to focus on companies that don't even need debt. Readers can access a list of growth stocks with zero net debt 100% free, right now.
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About SGX:5NV
Chasen Holdings
An investment holding company, provides logistics, and technical and engineering services in Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, the People’s Republic of China, India, and the United States.
Low risk and slightly overvalued.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



