CPMC Holdings (HKG:906) Takes On Some Risk With Its Use Of Debt
Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. As with many other companies CPMC Holdings Limited (HKG:906) makes use of debt. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
Check out our latest analysis for CPMC Holdings
What Is CPMC Holdings's Debt?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at June 2022 CPMC Holdings had debt of CN¥4.86b, up from CN¥4.31b in one year. However, it does have CN¥1.81b in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about CN¥3.05b.
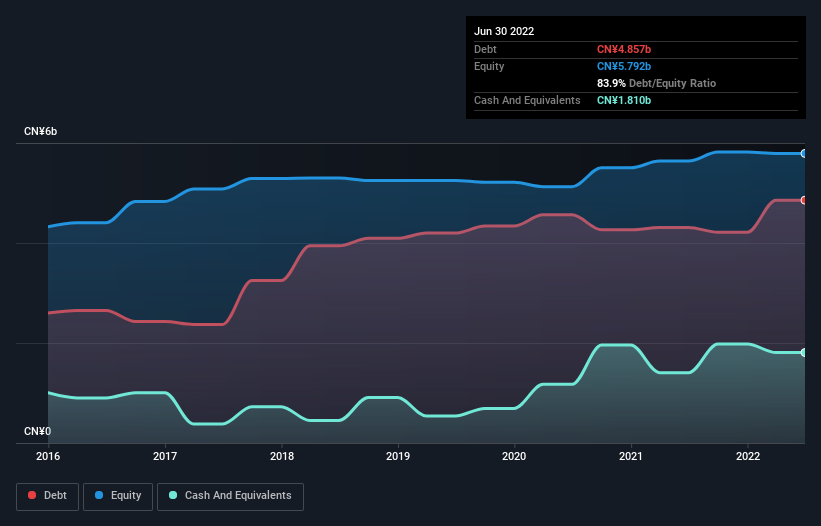
A Look At CPMC Holdings' Liabilities
We can see from the most recent balance sheet that CPMC Holdings had liabilities of CN¥6.28b falling due within a year, and liabilities of CN¥1.41b due beyond that. On the other hand, it had cash of CN¥1.81b and CN¥2.99b worth of receivables due within a year. So it has liabilities totalling CN¥2.90b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
This deficit is considerable relative to its market capitalization of CN¥3.63b, so it does suggest shareholders should keep an eye on CPMC Holdings' use of debt. This suggests shareholders would be heavily diluted if the company needed to shore up its balance sheet in a hurry.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
CPMC Holdings's net debt is 3.5 times its EBITDA, which is a significant but still reasonable amount of leverage. But its EBIT was about 1k times its interest expense, implying the company isn't really paying a high cost to maintain that level of debt. Even were the low cost to prove unsustainable, that is a good sign. The bad news is that CPMC Holdings saw its EBIT decline by 15% over the last year. If earnings continue to decline at that rate then handling the debt will be more difficult than taking three children under 5 to a fancy pants restaurant. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if CPMC Holdings can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, while the tax-man may adore accounting profits, lenders only accept cold hard cash. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. In the last three years, CPMC Holdings created free cash flow amounting to 7.8% of its EBIT, an uninspiring performance. For us, cash conversion that low sparks a little paranoia about is ability to extinguish debt.
Our View
On the face of it, CPMC Holdings's conversion of EBIT to free cash flow left us tentative about the stock, and its EBIT growth rate was no more enticing than the one empty restaurant on the busiest night of the year. But at least it's pretty decent at covering its interest expense with its EBIT; that's encouraging. Overall, we think it's fair to say that CPMC Holdings has enough debt that there are some real risks around the balance sheet. If all goes well, that should boost returns, but on the flip side, the risk of permanent capital loss is elevated by the debt. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. We've identified 2 warning signs with CPMC Holdings (at least 1 which is potentially serious) , and understanding them should be part of your investment process.
If you're interested in investing in businesses that can grow profits without the burden of debt, then check out this free list of growing businesses that have net cash on the balance sheet.
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About SEHK:906
CPMC Holdings
An investment holding company, manufactures and sells packaging products for various consumer goods in the People’s Republic of China.
Questionable track record with imperfect balance sheet.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



