Some say volatility, rather than debt, is the best way to think about risk as an investor, but Warren Buffett famously said that 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. As with many other companies Grainger plc (LON:GRI) makes use of debt. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. Part and parcel of capitalism is the process of 'creative destruction' where failed businesses are mercilessly liquidated by their bankers. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, debt can be an important tool in businesses, particularly capital heavy businesses. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for Grainger
What Is Grainger's Debt?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that as of March 2023 Grainger had UK£1.47b of debt, an increase on UK£1.35b, over one year. However, because it has a cash reserve of UK£70.5m, its net debt is less, at about UK£1.40b.
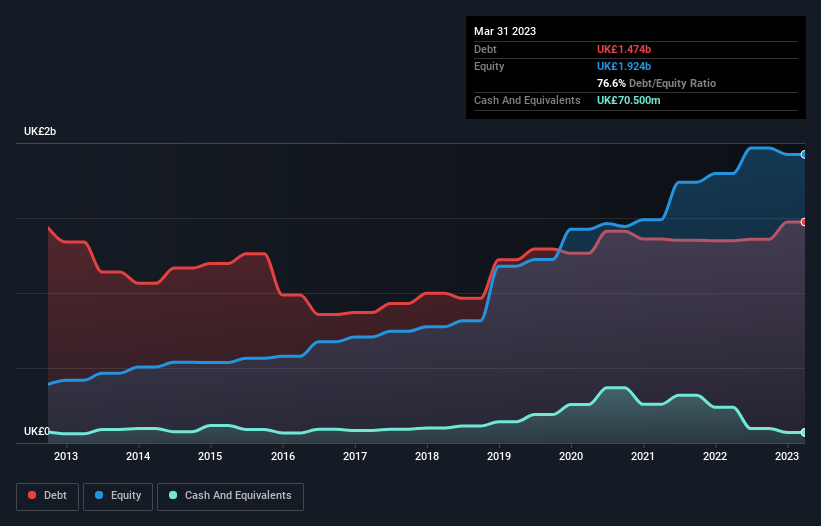
A Look At Grainger's Liabilities
The latest balance sheet data shows that Grainger had liabilities of UK£121.4m due within a year, and liabilities of UK£1.60b falling due after that. On the other hand, it had cash of UK£70.5m and UK£30.2m worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by UK£1.62b.
This is a mountain of leverage relative to its market capitalization of UK£1.75b. Should its lenders demand that it shore up the balance sheet, shareholders would likely face severe dilution.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Grainger has a rather high debt to EBITDA ratio of 11.0 which suggests a meaningful debt load. However, its interest coverage of 5.0 is reasonably strong, which is a good sign. Grainger grew its EBIT by 4.8% in the last year. Whilst that hardly knocks our socks off it is a positive when it comes to debt. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Grainger can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. Happily for any shareholders, Grainger actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT over the last three years. That sort of strong cash conversion gets us as excited as the crowd when the beat drops at a Daft Punk concert.
Our View
Neither Grainger's ability handle its debt, based on its EBITDA, nor its level of total liabilities gave us confidence in its ability to take on more debt. But the good news is it seems to be able to convert EBIT to free cash flow with ease. Looking at all the angles mentioned above, it does seem to us that Grainger is a somewhat risky investment as a result of its debt. That's not necessarily a bad thing, since leverage can boost returns on equity, but it is something to be aware of. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. For instance, we've identified 2 warning signs for Grainger (1 shouldn't be ignored) you should be aware of.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About LSE:GRI
Grainger
Designs, builds, develops, owns and operates rental homes in the United Kingdom.
Established dividend payer and good value.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



