
Some say volatility, rather than debt, is the best way to think about risk as an investor, but Warren Buffett famously said that 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. Importantly, CGG (EPA:CGG) does carry debt. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for CGG
What Is CGG's Debt?
The chart below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that CGG had US$1.16b in debt in December 2022; about the same as the year before. On the flip side, it has US$300.9m in cash leading to net debt of about US$855.6m.
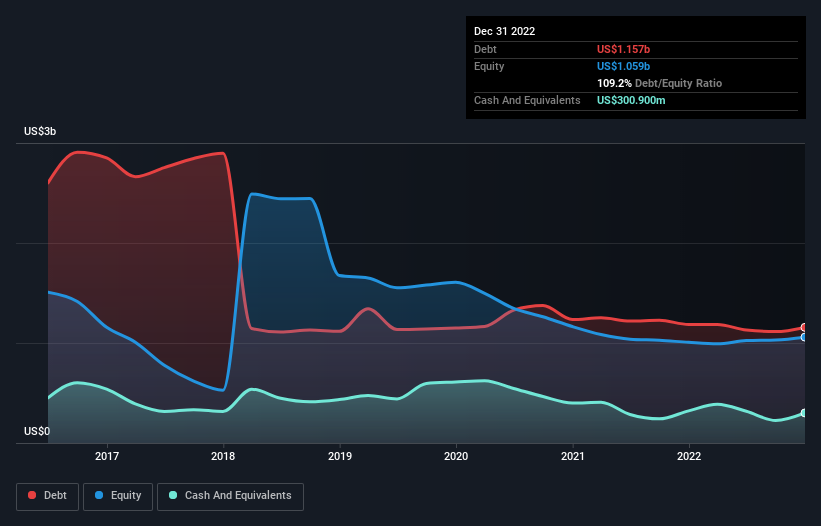
How Healthy Is CGG's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, CGG had liabilities of US$554.3m due within 12 months, and liabilities of US$1.28b due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of US$300.9m as well as receivables valued at US$422.8m due within 12 months. So its liabilities total US$1.11b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
This deficit casts a shadow over the US$528.4m company, like a colossus towering over mere mortals. So we'd watch its balance sheet closely, without a doubt. After all, CGG would likely require a major re-capitalisation if it had to pay its creditors today.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
While CGG has a quite reasonable net debt to EBITDA multiple of 2.2, its interest cover seems weak, at 1.6. In large part that's it has so much depreciation and amortisation. These charges may be non-cash, so they could be excluded when it comes to paying down debt. But the accounting charges are there for a reason -- some assets are seen to be losing value. Either way there's no doubt the stock is using meaningful leverage. It is well worth noting that CGG's EBIT shot up like bamboo after rain, gaining 55% in the last twelve months. That'll make it easier to manage its debt. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine CGG's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Looking at the most recent three years, CGG recorded free cash flow of 31% of its EBIT, which is weaker than we'd expect. That weak cash conversion makes it more difficult to handle indebtedness.
Our View
On the face of it, CGG's interest cover left us tentative about the stock, and its level of total liabilities was no more enticing than the one empty restaurant on the busiest night of the year. But on the bright side, its EBIT growth rate is a good sign, and makes us more optimistic. Looking at the bigger picture, it seems clear to us that CGG's use of debt is creating risks for the company. If everything goes well that may pay off but the downside of this debt is a greater risk of permanent losses. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. For instance, we've identified 3 warning signs for CGG (1 is potentially serious) you should be aware of.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About ENXTPA:VIRI
Viridien Société anonyme
Provides data, products, services, and solutions in Earth science, data science, sensing, and monitoring in North America, Latin America, the Central and South Americas, Europe, Africa, the Middle East, and the Asia Pacific.
Slight with moderate growth potential.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



