Howard Marks put it nicely when he said that, rather than worrying about share price volatility, 'The possibility of permanent loss is the risk I worry about... and every practical investor I know worries about.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. Importantly, Encavis AG (ETR:ECV) does carry debt. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. While that is not too common, we often do see indebted companies permanently diluting shareholders because lenders force them to raise capital at a distressed price. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
Check out our latest analysis for Encavis
How Much Debt Does Encavis Carry?
As you can see below, Encavis had €1.67b of debt, at June 2022, which is about the same as the year before. You can click the chart for greater detail. However, it also had €263.8m in cash, and so its net debt is €1.41b.
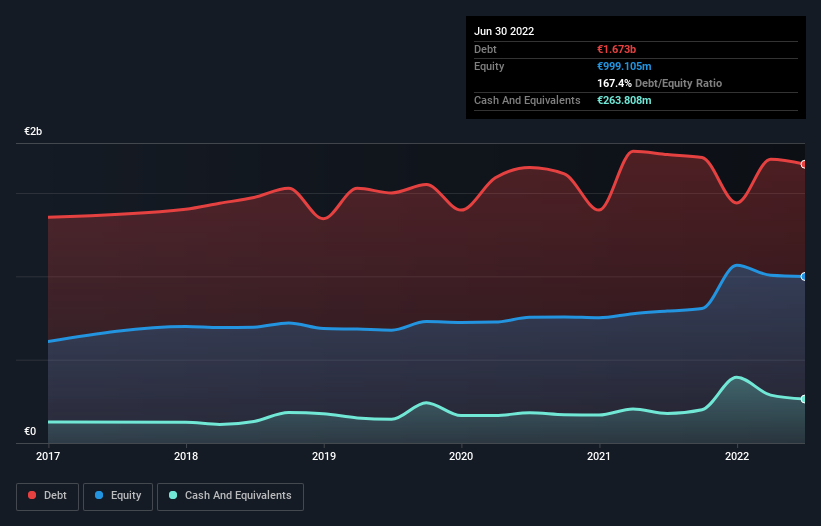
A Look At Encavis' Liabilities
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that Encavis had liabilities of €258.5m due within 12 months and liabilities of €1.95b due beyond that. Offsetting this, it had €263.8m in cash and €110.2m in receivables that were due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling €1.83b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
This deficit isn't so bad because Encavis is worth €3.57b, and thus could probably raise enough capital to shore up its balance sheet, if the need arose. But we definitely want to keep our eyes open to indications that its debt is bringing too much risk.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Encavis has a rather high debt to EBITDA ratio of 5.1 which suggests a meaningful debt load. But the good news is that it boasts fairly comforting interest cover of 2.8 times, suggesting it can responsibly service its obligations. Looking on the bright side, Encavis boosted its EBIT by a silky 79% in the last year. Like the milk of human kindness that sort of growth increases resilience, making the company more capable of managing debt. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Encavis's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. Happily for any shareholders, Encavis actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT over the last three years. There's nothing better than incoming cash when it comes to staying in your lenders' good graces.
Our View
Encavis's conversion of EBIT to free cash flow was a real positive on this analysis, as was its EBIT growth rate. In contrast, our confidence was undermined by its apparent struggle handle its debt, based on its EBITDA,. When we consider all the elements mentioned above, it seems to us that Encavis is managing its debt quite well. But a word of caution: we think debt levels are high enough to justify ongoing monitoring. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. To that end, you should learn about the 2 warning signs we've spotted with Encavis (including 1 which doesn't sit too well with us) .
When all is said and done, sometimes its easier to focus on companies that don't even need debt. Readers can access a list of growth stocks with zero net debt 100% free, right now.
The New Payments ETF Is Live on NASDAQ:
Money is moving to real-time rails, and a newly listed ETF now gives investors direct exposure. Fast settlement. Institutional custody. Simple access.
Explore how this launch could reshape portfolios
Sponsored ContentValuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Encavis might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About XTRA:ECV
Encavis
An independent power producer, acquires and operates solar and onshore wind parks in Germany, Italy, Spain, France, Denmark, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, Finland, Sweden, Ireland, and Lithuania.
Moderate growth potential with imperfect balance sheet.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Weekly Picks

Early mover in a fast growing industry. Likely to experience share price volatility as they scale


A case for CA$31.80 (undiluted), aka 8,616% upside from CA$0.37 (an 86 bagger!).


Moderation and Stabilisation: HOLD: Fair Price based on a 4-year Cycle is $12.08
Recently Updated Narratives


Title: Market Sentiment Is Dead Wrong — Here's Why PSEC Deserves a Second Look


An amazing opportunity to potentially get a 100 bagger

Amazon: Why the World’s Biggest Platform Still Runs on Invisible Economics
Popular Narratives


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026
Trending Discussion


