Warren Buffett famously said, 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. We can see that Bell Food Group AG (VTX:BELL) does use debt in its business. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Bell Food Group
How Much Debt Does Bell Food Group Carry?
The chart below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that Bell Food Group had CHF868.4m in debt in December 2020; about the same as the year before. However, it also had CHF180.5m in cash, and so its net debt is CHF687.9m.
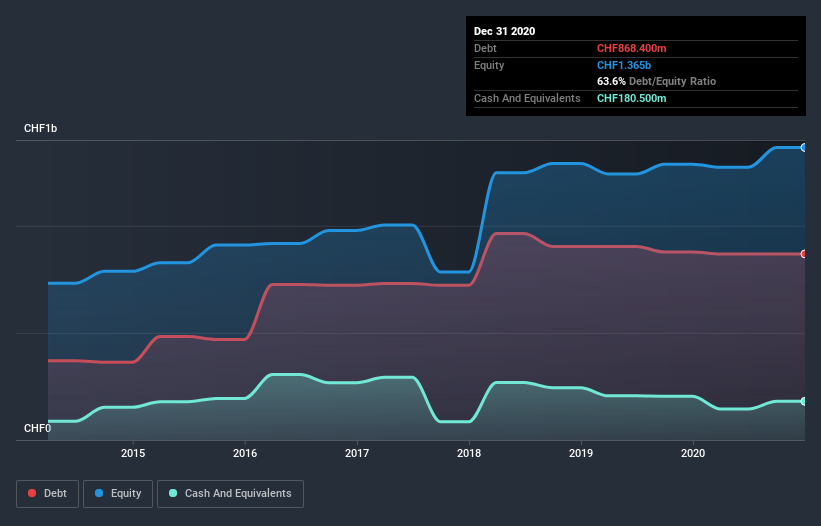
How Healthy Is Bell Food Group's Balance Sheet?
The latest balance sheet data shows that Bell Food Group had liabilities of CHF426.9m due within a year, and liabilities of CHF952.9m falling due after that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of CHF180.5m as well as receivables valued at CHF449.9m due within 12 months. So its liabilities total CHF749.4m more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
While this might seem like a lot, it is not so bad since Bell Food Group has a market capitalization of CHF1.60b, and so it could probably strengthen its balance sheet by raising capital if it needed to. However, it is still worthwhile taking a close look at its ability to pay off debt.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
Bell Food Group's net debt to EBITDA ratio of about 2.2 suggests only moderate use of debt. And its strong interest cover of 21.9 times, makes us even more comfortable. We note that Bell Food Group grew its EBIT by 28% in the last year, and that should make it easier to pay down debt, going forward. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Bell Food Group's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. In the last three years, Bell Food Group's free cash flow amounted to 32% of its EBIT, less than we'd expect. That weak cash conversion makes it more difficult to handle indebtedness.
Our View
Bell Food Group's interest cover was a real positive on this analysis, as was its EBIT growth rate. Having said that, its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow somewhat sensitizes us to potential future risks to the balance sheet. Considering this range of data points, we think Bell Food Group is in a good position to manage its debt levels. But a word of caution: we think debt levels are high enough to justify ongoing monitoring. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. To that end, you should learn about the 3 warning signs we've spotted with Bell Food Group (including 1 which shouldn't be ignored) .
When all is said and done, sometimes its easier to focus on companies that don't even need debt. Readers can access a list of growth stocks with zero net debt 100% free, right now.
If you decide to trade Bell Food Group, use the lowest-cost* platform that is rated #1 Overall by Barron’s, Interactive Brokers. Trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds on 135 markets, all from a single integrated account. Promoted
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Bell Food Group might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisThis article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About SWX:BELL
Bell Food Group
Engages in the processing of meat and convenience products in Switzerland.
Undervalued with excellent balance sheet.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives


Recently Updated Narratives

Constellation Energy Dividends and Growth

CoreWeave's Revenue Expected to Rocket 77.88% in 5-Year Forecast

Bisalloy Steel Group will shine with a projected profit margin increase of 12.8%
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026



