The external fund manager backed by Berkshire Hathaway's Charlie Munger, Li Lu, makes no bones about it when he says 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. We note that Soma Gold Corp. (CVE:SOMA) does have debt on its balance sheet. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
Check out our latest analysis for Soma Gold
How Much Debt Does Soma Gold Carry?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at March 2022 Soma Gold had debt of CA$19.6m, up from CA$16.4m in one year. And it doesn't have much cash, so its net debt is about the same.
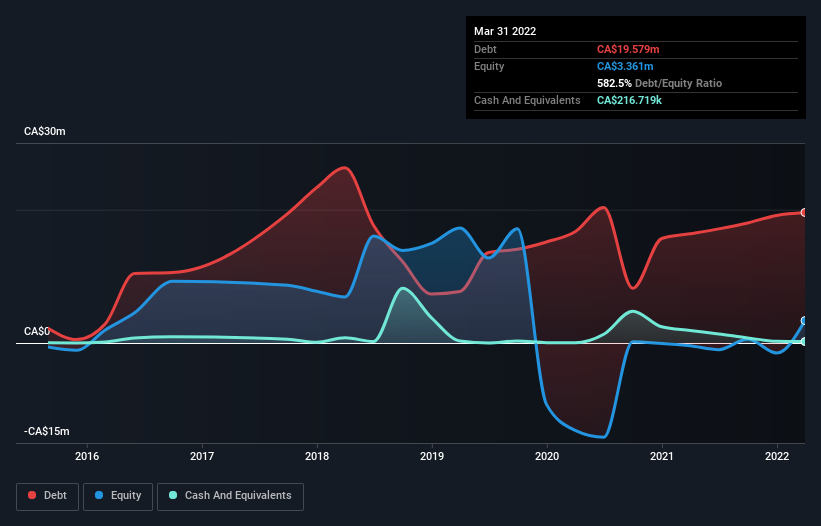
A Look At Soma Gold's Liabilities
The latest balance sheet data shows that Soma Gold had liabilities of CA$13.2m due within a year, and liabilities of CA$23.3m falling due after that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of CA$216.7k as well as receivables valued at CA$5.69m due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling CA$30.5m more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
When you consider that this deficiency exceeds the company's CA$27.2m market capitalization, you might well be inclined to review the balance sheet intently. Hypothetically, extremely heavy dilution would be required if the company were forced to pay down its liabilities by raising capital at the current share price.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
While Soma Gold has a quite reasonable net debt to EBITDA multiple of 1.7, its interest cover seems weak, at 1.5. This does suggest the company is paying fairly high interest rates. Either way there's no doubt the stock is using meaningful leverage. It is well worth noting that Soma Gold's EBIT shot up like bamboo after rain, gaining 46% in the last twelve months. That'll make it easier to manage its debt. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But you can't view debt in total isolation; since Soma Gold will need earnings to service that debt. So if you're keen to discover more about its earnings, it might be worth checking out this graph of its long term earnings trend.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. During the last two years, Soma Gold burned a lot of cash. While that may be a result of expenditure for growth, it does make the debt far more risky.
Our View
On the face of it, Soma Gold's interest cover left us tentative about the stock, and its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow was no more enticing than the one empty restaurant on the busiest night of the year. But at least it's pretty decent at growing its EBIT; that's encouraging. Looking at the bigger picture, it seems clear to us that Soma Gold's use of debt is creating risks for the company. If all goes well, that should boost returns, but on the flip side, the risk of permanent capital loss is elevated by the debt. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. For instance, we've identified 3 warning signs for Soma Gold that you should be aware of.
If, after all that, you're more interested in a fast growing company with a rock-solid balance sheet, then check out our list of net cash growth stocks without delay.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About TSXV:SOMA
Soma Gold
A natural resource company, engages in the acquisition, exploration, and development of mineral properties in Columbia.
Flawless balance sheet with acceptable track record.
Market Insights
Community Narratives


Recently Updated Narratives

Constellation Energy Dividends and Growth

CoreWeave's Revenue Expected to Rocket 77.88% in 5-Year Forecast

Bisalloy Steel Group will shine with a projected profit margin increase of 12.8%
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026



