Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. Importantly, Supremex Inc. (TSE:SXP) does carry debt. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Supremex
What Is Supremex's Debt?
As you can see below, at the end of December 2020, Supremex had CA$56.4m of debt, up from CA$53.5m a year ago. Click the image for more detail. On the flip side, it has CA$3.04m in cash leading to net debt of about CA$53.4m.
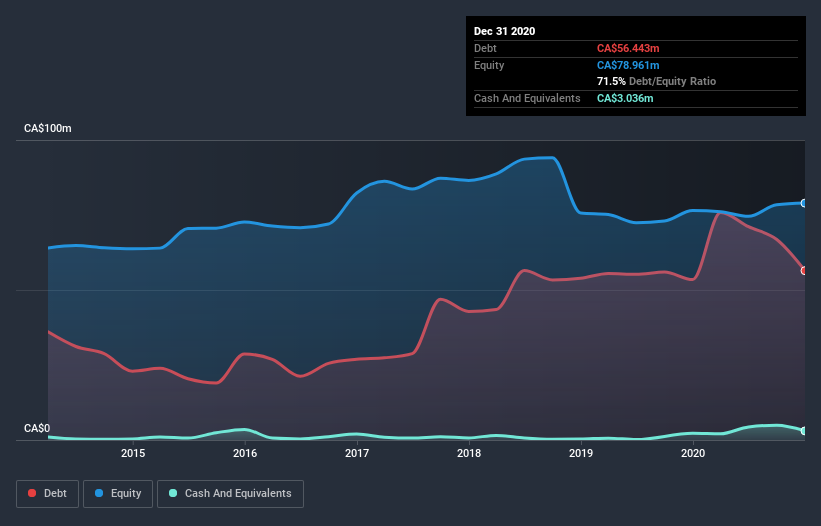
How Strong Is Supremex's Balance Sheet?
We can see from the most recent balance sheet that Supremex had liabilities of CA$32.4m falling due within a year, and liabilities of CA$75.2m due beyond that. On the other hand, it had cash of CA$3.04m and CA$27.2m worth of receivables due within a year. So it has liabilities totalling CA$77.3m more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
Given this deficit is actually higher than the company's market capitalization of CA$65.4m, we think shareholders really should watch Supremex's debt levels, like a parent watching their child ride a bike for the first time. Hypothetically, extremely heavy dilution would be required if the company were forced to pay down its liabilities by raising capital at the current share price.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Supremex's net debt is sitting at a very reasonable 2.0 times its EBITDA, while its EBIT covered its interest expense just 5.5 times last year. While that doesn't worry us too much, it does suggest the interest payments are somewhat of a burden. It is well worth noting that Supremex's EBIT shot up like bamboo after rain, gaining 32% in the last twelve months. That'll make it easier to manage its debt. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Supremex can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Over the last three years, Supremex actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT. That sort of strong cash conversion gets us as excited as the crowd when the beat drops at a Daft Punk concert.
Our View
Both Supremex's ability to to convert EBIT to free cash flow and its EBIT growth rate gave us comfort that it can handle its debt. But truth be told its level of total liabilities had us nibbling our nails. When we consider all the elements mentioned above, it seems to us that Supremex is managing its debt quite well. But a word of caution: we think debt levels are high enough to justify ongoing monitoring. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. For example Supremex has 4 warning signs (and 1 which is concerning) we think you should know about.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
If you decide to trade Supremex, use the lowest-cost* platform that is rated #1 Overall by Barron’s, Interactive Brokers. Trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds on 135 markets, all from a single integrated account. Promoted
The New Payments ETF Is Live on NASDAQ:
Money is moving to real-time rails, and a newly listed ETF now gives investors direct exposure. Fast settlement. Institutional custody. Simple access.
Explore how this launch could reshape portfolios
Sponsored ContentNew: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About TSX:SXP
Supremex
Manufactures and markets envelopes, and paper-based packaging solutions and specialty products for corporations, direct mailers, resellers, government entities, small and medium sized enterprises, and solution providers in Canada and the United States.
Excellent balance sheet and good value.
Market Insights
Weekly Picks

THE KINGDOM OF BROWN GOODS: WHY MGPI IS BEING CRUSHED BY INVENTORY & PRIMED FOR RESURRECTION


Why Vertical Aerospace (NYSE: EVTL) is Worth Possibly Over 13x its Current Price

The Quiet Giant That Became AI’s Power Grid
Recently Updated Narratives

Butler National (Buks) outperforms.


A tech powerhouse quietly powering the world’s AI infrastructure.


Keppel DC REIT (SGX: AJBU) is a resilient gem in the data center space.
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)





