Australian Vintage (ASX:AVG) Has A Somewhat Strained Balance Sheet
Howard Marks put it nicely when he said that, rather than worrying about share price volatility, 'The possibility of permanent loss is the risk I worry about... and every practical investor I know worries about. So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We can see that Australian Vintage Ltd (ASX:AVG) does use debt in its business. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Australian Vintage
What Is Australian Vintage's Debt?
As you can see below, Australian Vintage had AU$89.6m of debt, at December 2019, which is about the same as the year before. You can click the chart for greater detail. On the flip side, it has AU$11.2m in cash leading to net debt of about AU$78.4m.
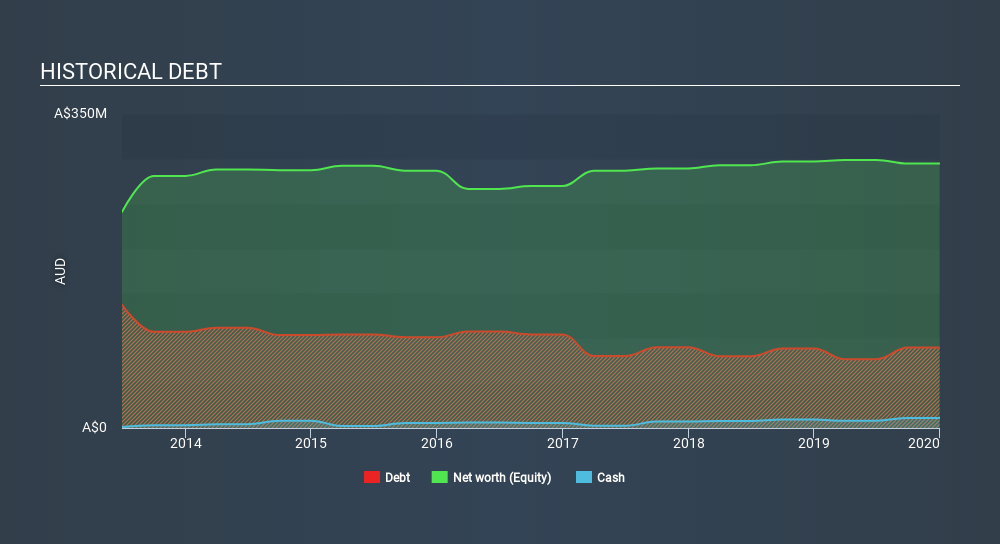
A Look At Australian Vintage's Liabilities
We can see from the most recent balance sheet that Australian Vintage had liabilities of AU$45.6m falling due within a year, and liabilities of AU$138.0m due beyond that. Offsetting this, it had AU$11.2m in cash and AU$55.7m in receivables that were due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by AU$116.6m.
When you consider that this deficiency exceeds the company's AU$112.3m market capitalization, you might well be inclined to review the balance sheet intently. Hypothetically, extremely heavy dilution would be required if the company were forced to pay down its liabilities by raising capital at the current share price.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
Australian Vintage's debt is 2.9 times its EBITDA, and its EBIT cover its interest expense 6.2 times over. Taken together this implies that, while we wouldn't want to see debt levels rise, we think it can handle its current leverage. Australian Vintage grew its EBIT by 2.9% in the last year. Whilst that hardly knocks our socks off it is a positive when it comes to debt. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Australian Vintage can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. In the last three years, Australian Vintage's free cash flow amounted to 25% of its EBIT, less than we'd expect. That weak cash conversion makes it more difficult to handle indebtedness.
Our View
Mulling over Australian Vintage's attempt at staying on top of its total liabilities, we're certainly not enthusiastic. Having said that, its ability to cover its interest expense with its EBIT isn't such a worry. Looking at the balance sheet and taking into account all these factors, we do believe that debt is making Australian Vintage stock a bit risky. That's not necessarily a bad thing, but we'd generally feel more comfortable with less leverage. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. Consider for instance, the ever-present spectre of investment risk. We've identified 3 warning signs with Australian Vintage , and understanding them should be part of your investment process.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
When trading Australian Vintage or any other investment, use the platform considered by many to be the Professional's Gateway to the Worlds Market, Interactive Brokers. You get the lowest-cost* trading on stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account.Promoted
Mobile Infrastructure for Defense and Disaster
The next wave in robotics isn't humanoid. Its fully autonomous towers delivering 5G, ISR, and radar in under 30 minutes, anywhere.
Get the investor briefing before the next round of contracts
Sponsored On Behalf of CiTechNew: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com.
About ASX:AVG
Australian Vintage
Produces, packages, markets, and distributes wine in Australia, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, Europe, the Americas, Asia, and internationally.
Mediocre balance sheet with low risk.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Weekly Picks

Early mover in a fast growing industry. Likely to experience share price volatility as they scale


A case for CA$31.80 (undiluted), aka 8,616% upside from CA$0.37 (an 86 bagger!).


Moderation and Stabilisation: HOLD: Fair Price based on a 4-year Cycle is $12.08
Recently Updated Narratives

Airbnb Stock: Platform Growth in a World of Saturation and Scrutiny

Adobe Stock: AI-Fueled ARR Growth Pushes Guidance Higher, But Cost Pressures Loom

Thomson Reuters Stock: When Legal Intelligence Becomes Mission-Critical Infrastructure
Popular Narratives


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026


The AI Infrastructure Giant Grows Into Its Valuation
Trending Discussion




