- United States
- /
- Electric Utilities
- /
- NYSE:PPL
Is PPL Corporation (NYSE:PPL) A Good Fit For Your Dividend Portfolio?

Could PPL Corporation (NYSE:PPL) be an attractive dividend share to own for the long haul? Investors are often drawn to strong companies with the idea of reinvesting the dividends. On the other hand, investors have been known to buy a stock because of its yield, and then lose money if the company's dividend doesn't live up to expectations.
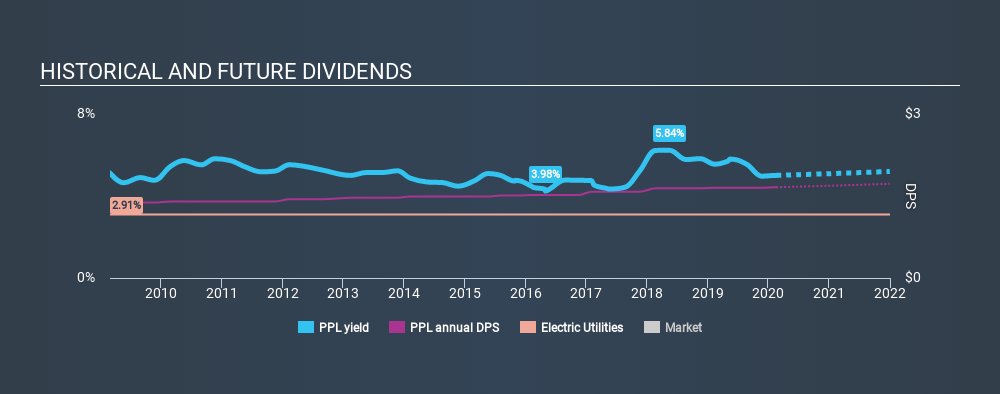
With PPL yielding 4.7% and having paid a dividend for over 10 years, many investors likely find the company quite interesting. We'd guess that plenty of investors have purchased it for the income. There are a few simple ways to reduce the risks of buying PPL for its dividend, and we'll go through these below.
Explore this interactive chart for our latest analysis on PPL!
Payout ratios
Dividends are typically paid from company earnings. If a company pays more in dividends than it earned, then the dividend might become unsustainable - hardly an ideal situation. Comparing dividend payments to a company's net profit after tax is a simple way of reality-checking whether a dividend is sustainable. Looking at the data, we can see that 66% of PPL's profits were paid out as dividends in the last 12 months. This is a healthy payout ratio, and while it does limit the amount of earnings that can be reinvested in the business, there is also some room to lift the payout ratio over time.
In addition to comparing dividends against profits, we should inspect whether the company generated enough cash to pay its dividend. Unfortunately, while PPL pays a dividend, it also reported negative free cash flow last year. While there may be a good reason for this, it's not ideal from a dividend perspective.
Is PPL's Balance Sheet Risky?
As PPL has a meaningful amount of debt, we need to check its balance sheet to see if the company might have debt risks. A rough way to check this is with these two simple ratios: a) net debt divided by EBITDA (earnings before interest, tax, depreciation and amortisation), and b) net interest cover. Net debt to EBITDA is a measure of a company's total debt. Net interest cover measures the ability to meet interest payments. Essentially we check that a) the company does not have too much debt, and b) that it can afford to pay the interest. With net debt of 5.12 times its EBITDA, PPL could be described as a highly leveraged company. While some companies can handle this level of leverage, we'd be concerned about the dividend sustainability if there was any risk of an earnings downturn.
We calculated its interest cover by measuring its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT), and dividing this by the company's net interest expense. Interest cover of 3.18 times its interest expense is starting to become a concern for PPL, and be aware that lenders may place additional restrictions on the company as well. High debt and weak interest cover are not a great combo, and we would be cautious of relying on this company's dividend while these metrics persist.
Consider getting our latest analysis on PPL's financial position here.
Dividend Volatility
One of the major risks of relying on dividend income, is the potential for a company to struggle financially and cut its dividend. Not only is your income cut, but the value of your investment declines as well - nasty. PPL has been paying dividends for a long time, but for the purpose of this analysis, we only examine the past 10 years of payments. During this period the dividend has been stable, which could imply the business could have relatively consistent earnings power. During the past ten-year period, the first annual payment was US$1.38 in 2010, compared to US$1.66 last year. Dividends per share have grown at approximately 1.9% per year over this time.
Dividends have grown relatively slowly, which is not great, but some investors may value the relative consistency of the dividend.
Dividend Growth Potential
While dividend payments have been relatively reliable, it would also be nice if earnings per share (EPS) were growing, as this is essential to maintaining the dividend's purchasing power over the long term. Earnings have grown at around 2.2% a year for the past five years, which is better than seeing them shrink! 2.2% per annum is not a particularly high rate of growth, which we find curious. When a business is not growing, it often makes more sense to pay higher dividends to shareholders rather than retain the cash with no way to utilise it.
Conclusion
To summarise, shareholders should always check that PPL's dividends are affordable, that its dividend payments are relatively stable, and that it has decent prospects for growing its earnings and dividend. First, the company has a payout ratio that was within an average range for most dividend stocks, but it paid out virtually all of its generated cash flow. Earnings growth has been limited, but we like that the dividend payments have been fairly consistent. In sum, we find it hard to get excited about PPL from a dividend perspective. It's not that we think it's a bad business; just that there are other companies that perform better on these criteria.
Earnings growth generally bodes well for the future value of company dividend payments. See if the 11 PPL analysts we track are forecasting continued growth with our free report on analyst estimates for the company.
Looking for more high-yielding dividend ideas? Try our curated list of dividend stocks with a yield above 3%.
If you spot an error that warrants correction, please contact the editor at editorial-team@simplywallst.com. This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Simply Wall St has no position in the stocks mentioned.
We aim to bring you long-term focused research analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Thank you for reading.
About NYSE:PPL
PPL
Provides electricity and natural gas to approximately 3.5 million customers in the United States.
Solid track record unattractive dividend payer.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives


