- Singapore
- /
- Retail Distributors
- /
- SGX:BFU
These 4 Measures Indicate That Tye Soon (SGX:BFU) Is Using Debt Extensively
Warren Buffett famously said, 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We note that Tye Soon Limited (SGX:BFU) does have debt on its balance sheet. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more common (but still painful) scenario is that it has to raise new equity capital at a low price, thus permanently diluting shareholders. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
Check out our latest analysis for Tye Soon
What Is Tye Soon's Debt?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that Tye Soon had S$65.8m of debt in December 2020, down from S$77.8m, one year before. However, it does have S$21.1m in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about S$44.7m.
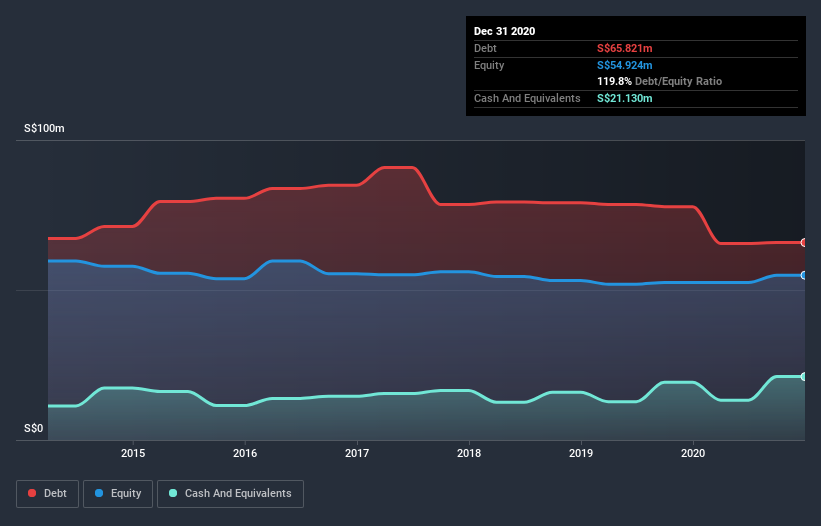
How Strong Is Tye Soon's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Tye Soon had liabilities of S$97.0m due within 12 months, and liabilities of S$9.11m due beyond 12 months. On the other hand, it had cash of S$21.1m and S$28.7m worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities total S$56.3m more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
The deficiency here weighs heavily on the S$7.85m company itself, as if a child were struggling under the weight of an enormous back-pack full of books, his sports gear, and a trumpet. So we'd watch its balance sheet closely, without a doubt. At the end of the day, Tye Soon would probably need a major re-capitalization if its creditors were to demand repayment.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Weak interest cover of 1.9 times and a disturbingly high net debt to EBITDA ratio of 8.8 hit our confidence in Tye Soon like a one-two punch to the gut. The debt burden here is substantial. However, one redeeming factor is that Tye Soon grew its EBIT at 17% over the last 12 months, boosting its ability to handle its debt. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But it is Tye Soon's earnings that will influence how the balance sheet holds up in the future. So if you're keen to discover more about its earnings, it might be worth checking out this graph of its long term earnings trend.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. Over the last three years, Tye Soon actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT. That sort of strong cash generation warms our hearts like a puppy in a bumblebee suit.
Our View
To be frank both Tye Soon's net debt to EBITDA and its track record of staying on top of its total liabilities make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. But at least it's pretty decent at converting EBIT to free cash flow; that's encouraging. Looking at the balance sheet and taking into account all these factors, we do believe that debt is making Tye Soon stock a bit risky. That's not necessarily a bad thing, but we'd generally feel more comfortable with less leverage. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. We've identified 3 warning signs with Tye Soon , and understanding them should be part of your investment process.
If you're interested in investing in businesses that can grow profits without the burden of debt, then check out this free list of growing businesses that have net cash on the balance sheet.
When trading Tye Soon or any other investment, use the platform considered by many to be the Professional's Gateway to the Worlds Market, Interactive Brokers. You get the lowest-cost* trading on stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account. Promoted
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Tye Soon might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisThis article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About SGX:BFU
Tye Soon
Imports, exports, and distributes automotive spare parts in Singapore, Malaysia, Australia, Thailand, Indonesia, Hong Kong/China, South Korea, and internationally.
Established dividend payer and good value.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



