The external fund manager backed by Berkshire Hathaway's Charlie Munger, Li Lu, makes no bones about it when he says 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. We can see that Thakral Corporation Ltd (SGX:AWI) does use debt in its business. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
See our latest analysis for Thakral
How Much Debt Does Thakral Carry?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at December 2020 Thakral had debt of S$52.3m, up from S$44.2m in one year. However, it also had S$27.5m in cash, and so its net debt is S$24.8m.
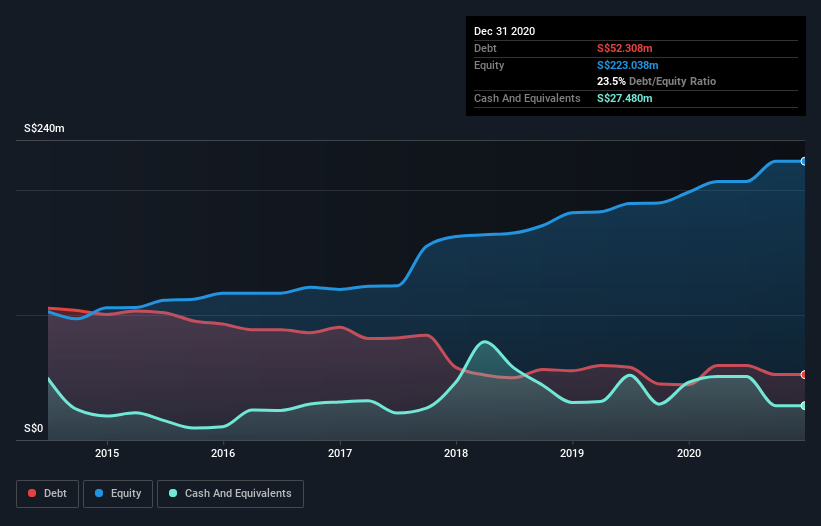
A Look At Thakral's Liabilities
According to the last reported balance sheet, Thakral had liabilities of S$57.5m due within 12 months, and liabilities of S$30.8m due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of S$27.5m as well as receivables valued at S$12.6m due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by S$48.2m.
This is a mountain of leverage relative to its market capitalization of S$61.5m. This suggests shareholders would be heavily diluted if the company needed to shore up its balance sheet in a hurry.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
While we wouldn't worry about Thakral's net debt to EBITDA ratio of 4.7, we think its super-low interest cover of 2.4 times is a sign of high leverage. It seems clear that the cost of borrowing money is negatively impacting returns for shareholders, of late. Worse, Thakral's EBIT was down 66% over the last year. If earnings continue to follow that trajectory, paying off that debt load will be harder than convincing us to run a marathon in the rain. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But you can't view debt in total isolation; since Thakral will need earnings to service that debt. So when considering debt, it's definitely worth looking at the earnings trend. Click here for an interactive snapshot.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Over the last three years, Thakral saw substantial negative free cash flow, in total. While that may be a result of expenditure for growth, it does make the debt far more risky.
Our View
To be frank both Thakral's conversion of EBIT to free cash flow and its track record of (not) growing its EBIT make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. And furthermore, its net debt to EBITDA also fails to instill confidence. Taking into account all the aforementioned factors, it looks like Thakral has too much debt. While some investors love that sort of risky play, it's certainly not our cup of tea. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. For example, we've discovered 2 warning signs for Thakral that you should be aware of before investing here.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
When trading Thakral or any other investment, use the platform considered by many to be the Professional's Gateway to the Worlds Market, Interactive Brokers. You get the lowest-cost* trading on stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account. Promoted
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Thakral might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisThis article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About SGX:AWI
Thakral
An investment holding company, markets and distributes beauty, fragrance, and lifestyle products in Singapore, India, rest of South Asia, the People’s Republic of China, North America, Australia, Japan, and internationally.
Solid track record with excellent balance sheet.
Market Insights
Community Narratives



