- New Zealand
- /
- Hospitality
- /
- NZSE:SVR
These 4 Measures Indicate That Savor (NZSE:SVR) Is Using Debt In A Risky Way
Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. We note that Savor Limited (NZSE:SVR) does have debt on its balance sheet. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more common (but still painful) scenario is that it has to raise new equity capital at a low price, thus permanently diluting shareholders. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
Our analysis indicates that SVR is potentially overvalued!
What Is Savor's Debt?
As you can see below, Savor had NZ$13.7m of debt, at September 2022, which is about the same as the year before. You can click the chart for greater detail. Net debt is about the same, since the it doesn't have much cash.
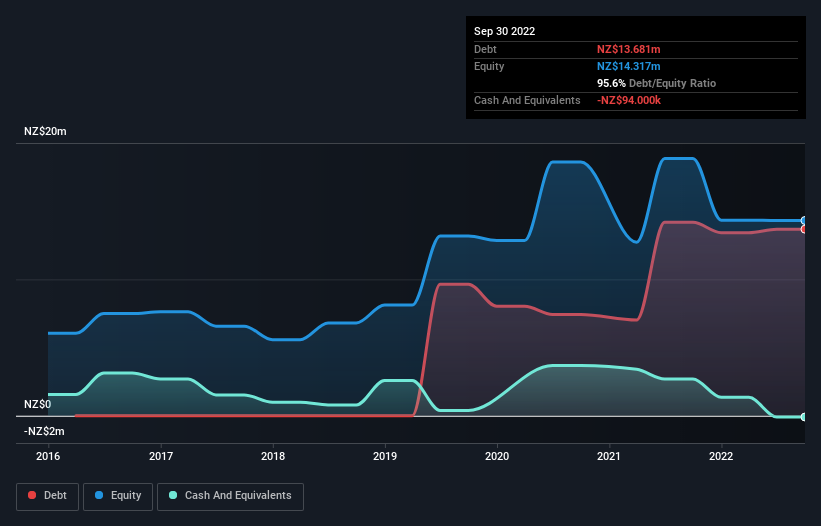
A Look At Savor's Liabilities
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that Savor had liabilities of NZ$14.9m due within 12 months and liabilities of NZ$25.6m due beyond that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of -NZ$94.0k as well as receivables valued at NZ$851.0k due within 12 months. So its liabilities total NZ$39.8m more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
The deficiency here weighs heavily on the NZ$24.7m company itself, as if a child were struggling under the weight of an enormous back-pack full of books, his sports gear, and a trumpet. So we'd watch its balance sheet closely, without a doubt. At the end of the day, Savor would probably need a major re-capitalization if its creditors were to demand repayment.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Savor shareholders face the double whammy of a high net debt to EBITDA ratio (6.7), and fairly weak interest coverage, since EBIT is just 0.21 times the interest expense. This means we'd consider it to have a heavy debt load. Worse, Savor's EBIT was down 70% over the last year. If earnings keep going like that over the long term, it has a snowball's chance in hell of paying off that debt. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But you can't view debt in total isolation; since Savor will need earnings to service that debt. So if you're keen to discover more about its earnings, it might be worth checking out this graph of its long term earnings trend.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. During the last three years, Savor produced sturdy free cash flow equating to 56% of its EBIT, about what we'd expect. This cold hard cash means it can reduce its debt when it wants to.
Our View
To be frank both Savor's EBIT growth rate and its track record of staying on top of its total liabilities make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. But at least it's pretty decent at converting EBIT to free cash flow; that's encouraging. After considering the datapoints discussed, we think Savor has too much debt. While some investors love that sort of risky play, it's certainly not our cup of tea. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. These risks can be hard to spot. Every company has them, and we've spotted 4 warning signs for Savor (of which 1 shouldn't be ignored!) you should know about.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About NZSE:SVR
Good value with mediocre balance sheet.
Market Insights
Community Narratives



