- India
- /
- Industrials
- /
- NSEI:NAVA
These 4 Measures Indicate That Nava (NSE:NAVA) Is Using Debt Reasonably Well
Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. As with many other companies Nava Limited (NSE:NAVA) makes use of debt. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
See our latest analysis for Nava
How Much Debt Does Nava Carry?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that Nava had ₹30.7b of debt in March 2023, down from ₹35.8b, one year before. However, because it has a cash reserve of ₹8.47b, its net debt is less, at about ₹22.2b.
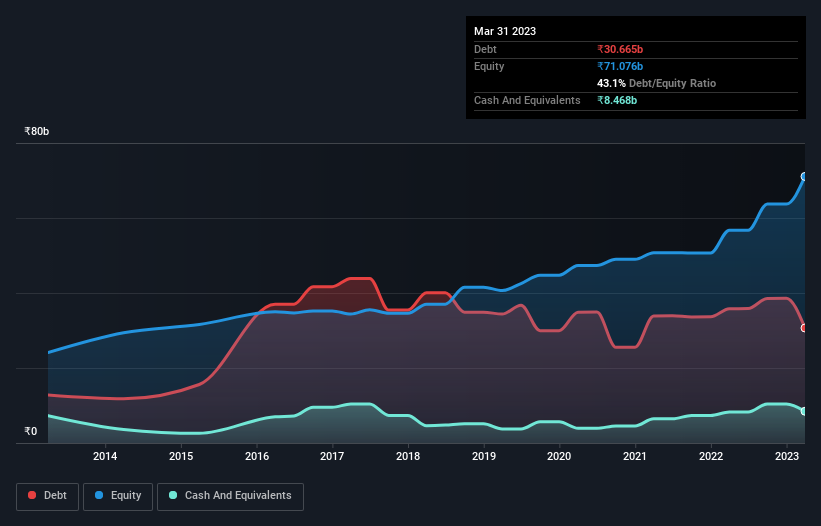
How Healthy Is Nava's Balance Sheet?
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that Nava had liabilities of ₹19.3b due within 12 months and liabilities of ₹21.2b due beyond that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of ₹8.47b as well as receivables valued at ₹23.4b due within 12 months. So its liabilities total ₹8.68b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
Nava has a market capitalization of ₹38.8b, so it could very likely raise cash to ameliorate its balance sheet, if the need arose. But we definitely want to keep our eyes open to indications that its debt is bringing too much risk.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
While Nava's low debt to EBITDA ratio of 1.4 suggests only modest use of debt, the fact that EBIT only covered the interest expense by 6.3 times last year does give us pause. But the interest payments are certainly sufficient to have us thinking about how affordable its debt is. Another good sign is that Nava has been able to increase its EBIT by 23% in twelve months, making it easier to pay down debt. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But it is Nava's earnings that will influence how the balance sheet holds up in the future. So if you're keen to discover more about its earnings, it might be worth checking out this graph of its long term earnings trend.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. During the last three years, Nava produced sturdy free cash flow equating to 78% of its EBIT, about what we'd expect. This cold hard cash means it can reduce its debt when it wants to.
Our View
The good news is that Nava's demonstrated ability to convert EBIT to free cash flow delights us like a fluffy puppy does a toddler. And the good news does not stop there, as its EBIT growth rate also supports that impression! Looking at the bigger picture, we think Nava's use of debt seems quite reasonable and we're not concerned about it. While debt does bring risk, when used wisely it can also bring a higher return on equity. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. To that end, you should be aware of the 1 warning sign we've spotted with Nava .
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Nava might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About NSEI:NAVA
Nava
Engages in ferroalloy manufacturing, energy, mining, agribusiness, and operation and maintenance services in India, Zambia, the United States, Hong Kong, Japan, the United Arab Emirates, and internationally.
Flawless balance sheet established dividend payer.
Market Insights
Community Narratives



