Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We can see that Mitchells & Butlers plc (LON:MAB) does use debt in its business. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
View our latest analysis for Mitchells & Butlers
How Much Debt Does Mitchells & Butlers Carry?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that Mitchells & Butlers had debt of UK£1.28b at the end of April 2024, a reduction from UK£1.45b over a year. However, because it has a cash reserve of UK£194.0m, its net debt is less, at about UK£1.09b.
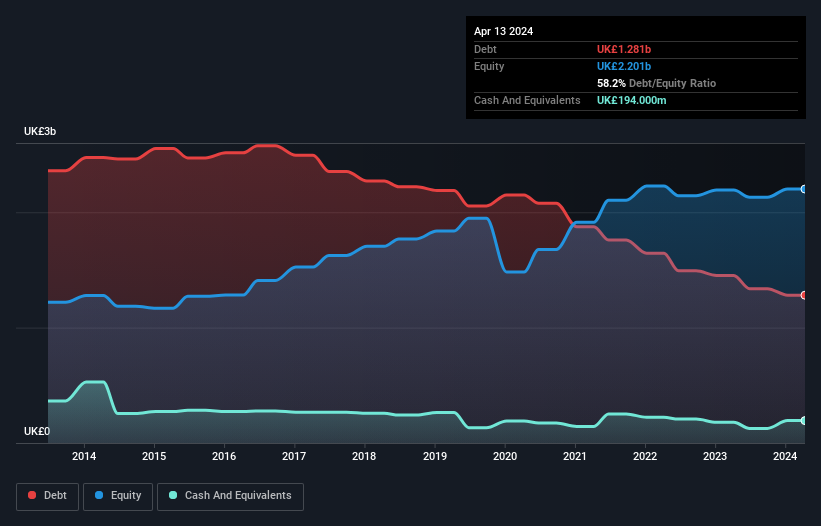
A Look At Mitchells & Butlers' Liabilities
The latest balance sheet data shows that Mitchells & Butlers had liabilities of UK£674.0m due within a year, and liabilities of UK£1.94b falling due after that. On the other hand, it had cash of UK£194.0m and UK£93.0m worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities total UK£2.33b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
When you consider that this deficiency exceeds the company's UK£1.75b market capitalization, you might well be inclined to review the balance sheet intently. Hypothetically, extremely heavy dilution would be required if the company were forced to pay down its liabilities by raising capital at the current share price.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Mitchells & Butlers's debt is 2.8 times its EBITDA, and its EBIT cover its interest expense 2.7 times over. Taken together this implies that, while we wouldn't want to see debt levels rise, we think it can handle its current leverage. The good news is that Mitchells & Butlers grew its EBIT a smooth 33% over the last twelve months. Like the milk of human kindness that sort of growth increases resilience, making the company more capable of managing debt. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Mitchells & Butlers can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. Over the last three years, Mitchells & Butlers recorded free cash flow worth a fulsome 100% of its EBIT, which is stronger than we'd usually expect. That puts it in a very strong position to pay down debt.
Our View
Both Mitchells & Butlers's ability to to convert EBIT to free cash flow and its EBIT growth rate gave us comfort that it can handle its debt. But truth be told its level of total liabilities had us nibbling our nails. Looking at all this data makes us feel a little cautious about Mitchells & Butlers's debt levels. While we appreciate debt can enhance returns on equity, we'd suggest that shareholders keep close watch on its debt levels, lest they increase. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. Case in point: We've spotted 2 warning signs for Mitchells & Butlers you should be aware of, and 1 of them shouldn't be ignored.
If you're interested in investing in businesses that can grow profits without the burden of debt, then check out this free list of growing businesses that have net cash on the balance sheet.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com
About LSE:MAB
Mitchells & Butlers
Engages in the management of pubs, bars, and restaurants in the United Kingdom and Germany.
Solid track record and good value.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



