Howard Marks put it nicely when he said that, rather than worrying about share price volatility, 'The possibility of permanent loss is the risk I worry about... and every practical investor I know worries about.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. We can see that Audax Renovables, S.A. (BME:ADX) does use debt in its business. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for Audax Renovables
What Is Audax Renovables's Net Debt?
As you can see below, Audax Renovables had €641.7m of debt at December 2022, down from €773.2m a year prior. However, it also had €322.5m in cash, and so its net debt is €319.3m.
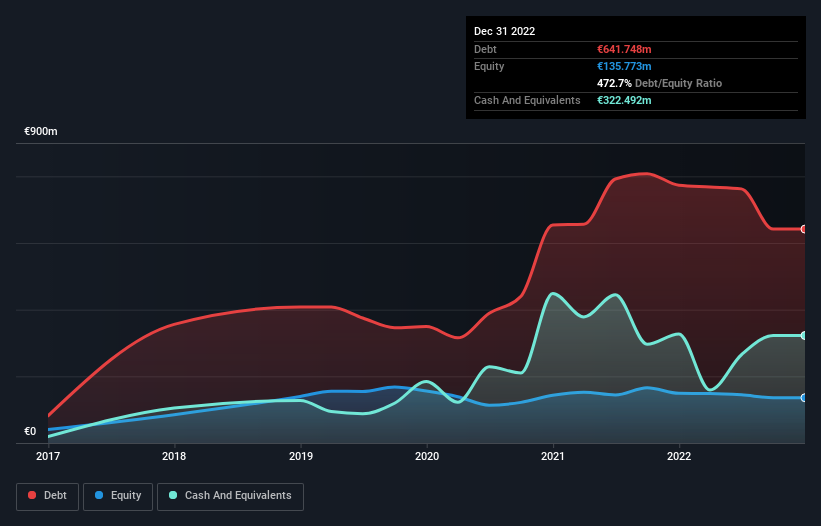
How Healthy Is Audax Renovables' Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Audax Renovables had liabilities of €535.8m due within 12 months, and liabilities of €645.2m due beyond 12 months. Offsetting this, it had €322.5m in cash and €308.5m in receivables that were due within 12 months. So its liabilities total €550.1m more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
When you consider that this deficiency exceeds the company's €520.4m market capitalization, you might well be inclined to review the balance sheet intently. In the scenario where the company had to clean up its balance sheet quickly, it seems likely shareholders would suffer extensive dilution.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Weak interest cover of 1.2 times and a disturbingly high net debt to EBITDA ratio of 6.2 hit our confidence in Audax Renovables like a one-two punch to the gut. The debt burden here is substantial. More concerning, Audax Renovables saw its EBIT drop by 4.2% in the last twelve months. If that earnings trend continues the company will face an uphill battle to pay off its debt. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Audax Renovables can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, while the tax-man may adore accounting profits, lenders only accept cold hard cash. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. Over the most recent three years, Audax Renovables recorded free cash flow worth 57% of its EBIT, which is around normal, given free cash flow excludes interest and tax. This cold hard cash means it can reduce its debt when it wants to.
Our View
To be frank both Audax Renovables's net debt to EBITDA and its track record of covering its interest expense with its EBIT make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. But on the bright side, its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow is a good sign, and makes us more optimistic. We're quite clear that we consider Audax Renovables to be really rather risky, as a result of its balance sheet health. So we're almost as wary of this stock as a hungry kitten is about falling into its owner's fish pond: once bitten, twice shy, as they say. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. To that end, you should learn about the 3 warning signs we've spotted with Audax Renovables (including 1 which is a bit concerning) .
If, after all that, you're more interested in a fast growing company with a rock-solid balance sheet, then check out our list of net cash growth stocks without delay.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About BME:ADX
Audax Renovables
Engages in the generation and supplying of renewable electricity and gas in Spain, Portugal, Italy, Poland, Germany, Netherlands, France, Panama, and Hungary.
Adequate balance sheet and fair value.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives


Recently Updated Narratives


MINISO's fair value is projected at 26.69 with an anticipated PE ratio shift of 20x

The Quiet Giant That Became AI’s Power Grid


Nova Ljubljanska Banka d.d will expect a 11.2% revenue boost driving future growth
Popular Narratives


The company that turned a verb into a global necessity and basically runs the modern internet, digital ads, smartphones, maps, and AI.


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success



