- China
- /
- Semiconductors
- /
- SHSE:600460
These 4 Measures Indicate That Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd (SHSE:600460) Is Using Debt Extensively
Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. Importantly, Hangzhou Silan Microelectronics Co.,Ltd (SHSE:600460) does carry debt. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. Part and parcel of capitalism is the process of 'creative destruction' where failed businesses are mercilessly liquidated by their bankers. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Having said that, the most common situation is where a company manages its debt reasonably well - and to its own advantage. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
Check out our latest analysis for Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd
What Is Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd's Debt?
As you can see below, Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd had CN¥5.97b of debt, at September 2024, which is about the same as the year before. You can click the chart for greater detail. However, it also had CN¥4.70b in cash, and so its net debt is CN¥1.27b.
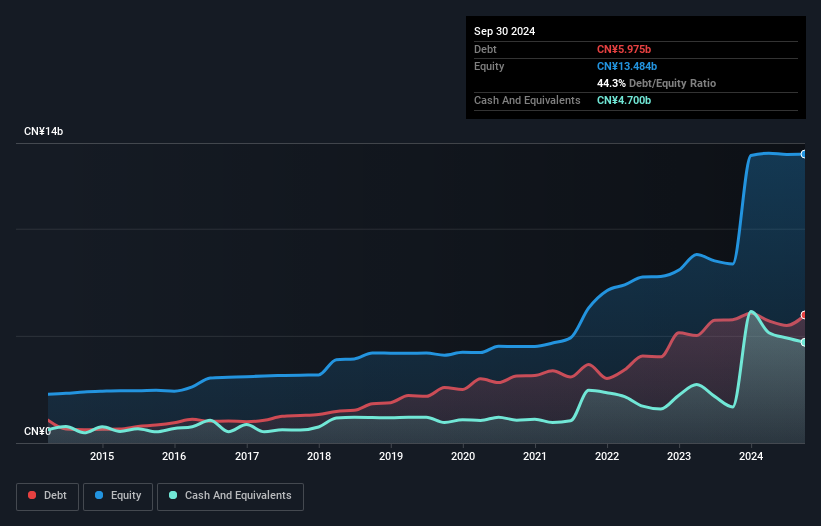
A Look At Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd's Liabilities
According to the last reported balance sheet, Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd had liabilities of CN¥6.95b due within 12 months, and liabilities of CN¥3.76b due beyond 12 months. On the other hand, it had cash of CN¥4.70b and CN¥4.36b worth of receivables due within a year. So it has liabilities totalling CN¥1.65b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
Of course, Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd has a market capitalization of CN¥41.1b, so these liabilities are probably manageable. However, we do think it is worth keeping an eye on its balance sheet strength, as it may change over time.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd's net debt is only 0.95 times its EBITDA. And its EBIT easily covers its interest expense, being 15.3 times the size. So we're pretty relaxed about its super-conservative use of debt. The modesty of its debt load may become crucial for Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd if management cannot prevent a repeat of the 49% cut to EBIT over the last year. When it comes to paying off debt, falling earnings are no more useful than sugary sodas are for your health. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, while the tax-man may adore accounting profits, lenders only accept cold hard cash. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. During the last three years, Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd burned a lot of cash. While that may be a result of expenditure for growth, it does make the debt far more risky.
Our View
Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd's EBIT growth rate and conversion of EBIT to free cash flow definitely weigh on it, in our esteem. But the good news is it seems to be able to cover its interest expense with its EBIT with ease. When we consider all the factors discussed, it seems to us that Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd is taking some risks with its use of debt. While that debt can boost returns, we think the company has enough leverage now. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. For example, we've discovered 1 warning sign for Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd that you should be aware of before investing here.
When all is said and done, sometimes its easier to focus on companies that don't even need debt. Readers can access a list of growth stocks with zero net debt 100% free, right now.
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About SHSE:600460
Hangzhou Silan MicroelectronicsLtd
Designs, manufactures, and sells integrated circuit (IC) chips and semiconductor microelectronics-related products in China.
Excellent balance sheet with proven track record.
Market Insights
Community Narratives



