- Switzerland
- /
- Food
- /
- SWX:BELL
These 4 Measures Indicate That Bell Food Group (VTX:BELL) Is Using Debt Reasonably Well
Some say volatility, rather than debt, is the best way to think about risk as an investor, but Warren Buffett famously said that 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. Importantly, Bell Food Group AG (VTX:BELL) does carry debt. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. While that is not too common, we often do see indebted companies permanently diluting shareholders because lenders force them to raise capital at a distressed price. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Bell Food Group
How Much Debt Does Bell Food Group Carry?
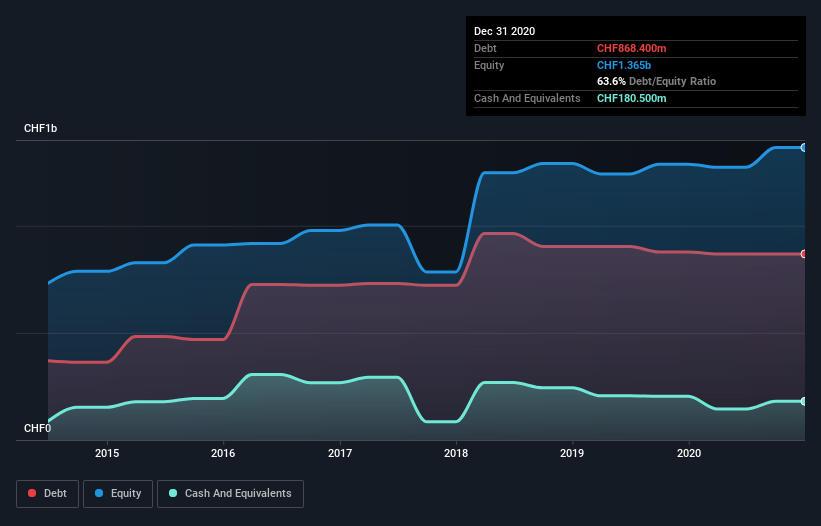
As you can see below, Bell Food Group had CHF868.4m of debt, at December 2020, which is about the same as the year before. You can click the chart for greater detail. On the flip side, it has CHF180.5m in cash leading to net debt of about CHF687.9m.
How Strong Is Bell Food Group's Balance Sheet?
The latest balance sheet data shows that Bell Food Group had liabilities of CHF426.9m due within a year, and liabilities of CHF952.9m falling due after that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of CHF180.5m as well as receivables valued at CHF449.9m due within 12 months. So its liabilities total CHF749.4m more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
While this might seem like a lot, it is not so bad since Bell Food Group has a market capitalization of CHF1.76b, and so it could probably strengthen its balance sheet by raising capital if it needed to. But it's clear that we should definitely closely examine whether it can manage its debt without dilution.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
Bell Food Group's net debt to EBITDA ratio of about 2.2 suggests only moderate use of debt. And its strong interest cover of 21.9 times, makes us even more comfortable. Also relevant is that Bell Food Group has grown its EBIT by a very respectable 28% in the last year, thus enhancing its ability to pay down debt. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Bell Food Group's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. In the last three years, Bell Food Group's free cash flow amounted to 32% of its EBIT, less than we'd expect. That weak cash conversion makes it more difficult to handle indebtedness.
Our View
The good news is that Bell Food Group's demonstrated ability to cover its interest expense with its EBIT delights us like a fluffy puppy does a toddler. But, on a more sombre note, we are a little concerned by its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow. All these things considered, it appears that Bell Food Group can comfortably handle its current debt levels. On the plus side, this leverage can boost shareholder returns, but the potential downside is more risk of loss, so it's worth monitoring the balance sheet. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. These risks can be hard to spot. Every company has them, and we've spotted 2 warning signs for Bell Food Group you should know about.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
When trading Bell Food Group or any other investment, use the platform considered by many to be the Professional's Gateway to the Worlds Market, Interactive Brokers. You get the lowest-cost* trading on stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account. Promoted
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Bell Food Group might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisThis article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About SWX:BELL
Bell Food Group
Engages in the processing of meat and convenience products in Switzerland.
Undervalued with excellent balance sheet.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives


Recently Updated Narratives


MINISO's fair value is projected at 26.69 with an anticipated PE ratio shift of 20x

The Quiet Giant That Became AI’s Power Grid


Nova Ljubljanska Banka d.d will expect a 11.2% revenue boost driving future growth
Popular Narratives


The company that turned a verb into a global necessity and basically runs the modern internet, digital ads, smartphones, maps, and AI.


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success



