Warren Buffett famously said, 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. As with many other companies BCE Inc. (TSE:BCE) makes use of debt. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Having said that, the most common situation is where a company manages its debt reasonably well - and to its own advantage. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for BCE
What Is BCE's Debt?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at September 2024 BCE had debt of CA$40.1b, up from CA$34.7b in one year. However, it does have CA$2.61b in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about CA$37.5b.
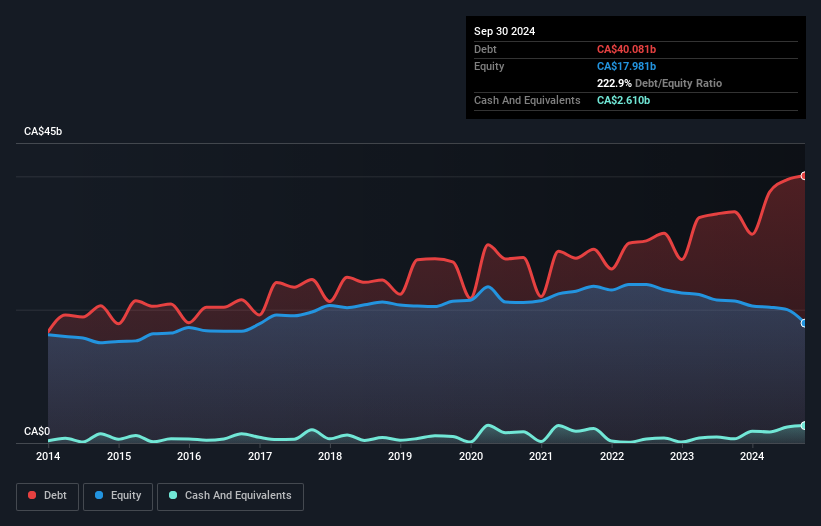
How Healthy Is BCE's Balance Sheet?
The latest balance sheet data shows that BCE had liabilities of CA$14.1b due within a year, and liabilities of CA$40.6b falling due after that. Offsetting this, it had CA$2.61b in cash and CA$4.44b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So its liabilities total CA$47.7b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
This deficit casts a shadow over the CA$30.0b company, like a colossus towering over mere mortals. So we definitely think shareholders need to watch this one closely. At the end of the day, BCE would probably need a major re-capitalization if its creditors were to demand repayment.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
BCE has a debt to EBITDA ratio of 4.3 and its EBIT covered its interest expense 3.6 times. Taken together this implies that, while we wouldn't want to see debt levels rise, we think it can handle its current leverage. Notably, BCE's EBIT was pretty flat over the last year, which isn't ideal given the debt load. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine BCE's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. Looking at the most recent three years, BCE recorded free cash flow of 40% of its EBIT, which is weaker than we'd expect. That weak cash conversion makes it more difficult to handle indebtedness.
Our View
Mulling over BCE's attempt at staying on top of its total liabilities, we're certainly not enthusiastic. But at least its EBIT growth rate is not so bad. Overall, it seems to us that BCE's balance sheet is really quite a risk to the business. For this reason we're pretty cautious about the stock, and we think shareholders should keep a close eye on its liquidity. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. Case in point: We've spotted 5 warning signs for BCE you should be aware of, and 2 of them make us uncomfortable.
When all is said and done, sometimes its easier to focus on companies that don't even need debt. Readers can access a list of growth stocks with zero net debt 100% free, right now.
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if BCE might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About TSX:BCE
BCE
A communications company, provides wireless, wireline, internet, streaming services, and television (TV) services to residential, business, and wholesale customers in Canada.
Undervalued with slight risk.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



