Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. Importantly, Arbonia AG (VTX:ARBN) does carry debt. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Having said that, the most common situation is where a company manages its debt reasonably well - and to its own advantage. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for Arbonia
What Is Arbonia's Net Debt?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at June 2024 Arbonia had debt of CHF348.3m, up from CHF266.1m in one year. On the flip side, it has CHF19.3m in cash leading to net debt of about CHF329.0m.
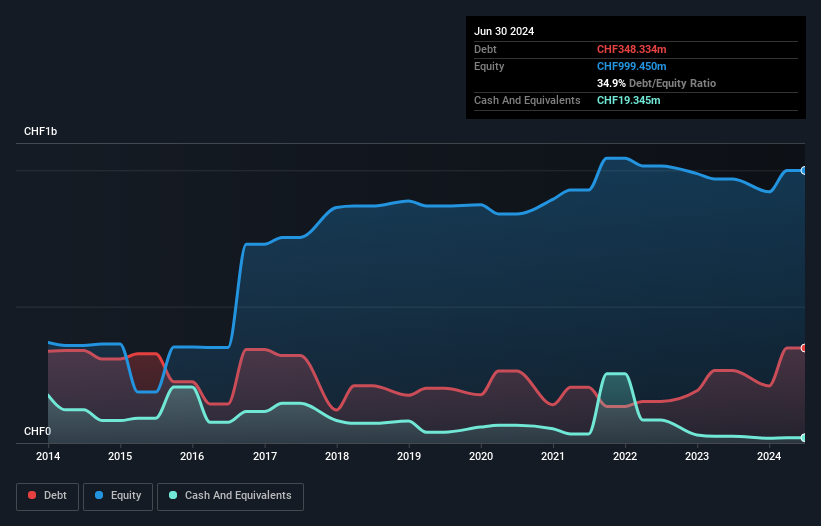
How Strong Is Arbonia's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Arbonia had liabilities of CHF672.3m due within 12 months, and liabilities of CHF99.7m due beyond 12 months. On the other hand, it had cash of CHF19.3m and CHF104.7m worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by CHF647.9m.
This deficit is considerable relative to its market capitalization of CHF794.5m, so it does suggest shareholders should keep an eye on Arbonia's use of debt. This suggests shareholders would be heavily diluted if the company needed to shore up its balance sheet in a hurry.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
While Arbonia's debt to EBITDA ratio (4.4) suggests that it uses some debt, its interest cover is very weak, at 2.4, suggesting high leverage. It seems that the business incurs large depreciation and amortisation charges, so maybe its debt load is heavier than it would first appear, since EBITDA is arguably a generous measure of earnings. So shareholders should probably be aware that interest expenses appear to have really impacted the business lately. However, the silver lining was that Arbonia achieved a positive EBIT of CHF22m in the last twelve months, an improvement on the prior year's loss. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Arbonia's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So it is important to check how much of its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) converts to actual free cash flow. Considering the last year, Arbonia actually recorded a cash outflow, overall. Debt is usually more expensive, and almost always more risky in the hands of a company with negative free cash flow. Shareholders ought to hope for an improvement.
Our View
To be frank both Arbonia's interest cover and its track record of converting EBIT to free cash flow make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. But at least its EBIT growth rate is not so bad. We're quite clear that we consider Arbonia to be really rather risky, as a result of its balance sheet health. So we're almost as wary of this stock as a hungry kitten is about falling into its owner's fish pond: once bitten, twice shy, as they say. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. For example, we've discovered 2 warning signs for Arbonia (1 is concerning!) that you should be aware of before investing here.
If, after all that, you're more interested in a fast growing company with a rock-solid balance sheet, then check out our list of net cash growth stocks without delay.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About SWX:ARBN
Arbonia
Engages in supply of interior doors crafted from wood and glass in in Switzerland and internationally.
Reasonable growth potential and fair value.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



